Difference between revisions of "ICT student textbook/How is a computer different from a fridge"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (1 revision imported) |
|||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
{{font color|brown|In this activity, you will develop an appreciation of what the computer is and what makes the computer work.}} | {{font color|brown|In this activity, you will develop an appreciation of what the computer is and what makes the computer work.}} | ||
| − | === | + | ===Objectives=== |
| − | + | # Getting introduced to the ICT environment | |
| + | # Understanding the role of hardware and software and what makes digital ICT special | ||
===What prior skills are assumed=== | ===What prior skills are assumed=== | ||
| Line 31: | Line 32: | ||
===Description of activity with detailed steps=== | ===Description of activity with detailed steps=== | ||
====Teacher-led component==== | ====Teacher-led component==== | ||
| − | #Your teacher may ask you, in small groups, to make a of list all the | + | #Your teacher may ask you, in small groups, to make a of list all the things a fridge does and a list of all the things you think a computer can do. |
#In a group activity your teacher will compile all the group comments in a digital mind map using a [[Learn_Freeplane|concept mapping]] tool, called [[Learn Freeplane|Freeplane.]] She will encourage you to classify the various things the computer will do. | #In a group activity your teacher will compile all the group comments in a digital mind map using a [[Learn_Freeplane|concept mapping]] tool, called [[Learn Freeplane|Freeplane.]] She will encourage you to classify the various things the computer will do. | ||
| − | #The teacher will discuss why an operating system needed | + | #The teacher will discuss why an operating system is needed and how it works with different applications, for processing your inputs and providing outputs. |
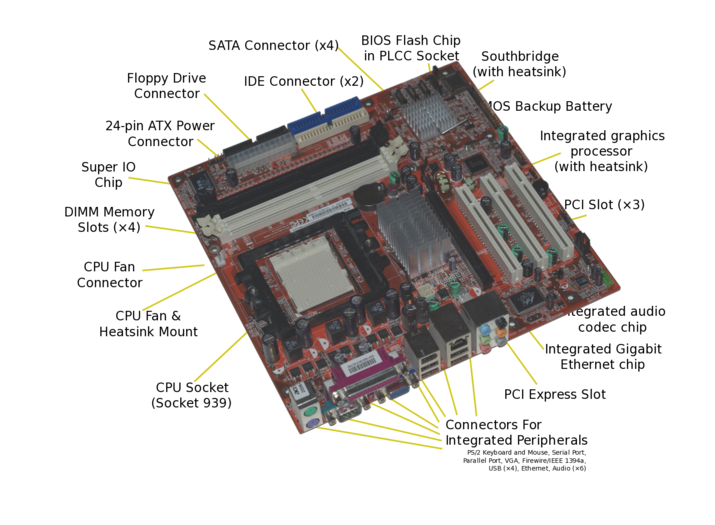
| − | #With the help of | + | #With the help of an image, the teacher will discuss the parts of a [[Explore_a_computer|computer]]. |
| − | <gallery mode=packed heights=350px style="text-align:left"> | + | <gallery mode="packed" heights="350px" style="text-align:left"> |
File:Operating system placement.svg|'''What does an operating system do''' | File:Operating system placement.svg|'''What does an operating system do''' | ||
File:Personal computer, exploded.svg|'''What does a personal computer contain''' | File:Personal computer, exploded.svg|'''What does a personal computer contain''' | ||
Revision as of 23:25, 6 June 2017
How is a computer different from a fridge
In this activity, you will develop an appreciation of what the computer is and what makes the computer work.
Objectives
- Getting introduced to the ICT environment
- Understanding the role of hardware and software and what makes digital ICT special
What prior skills are assumed
This is your first activity in the textbook. Enjoy the new subject!!
What resources do you need
- Working computer lab with projector
- Computers installed with Ubuntu Operating System
- Images to show of the computer
- Handout for Basic digital literacy
- Handout for Freeplane
What digital skills will you learn
- Getting familiar with the ICT environment and different kinds of ICT devices
- Operating a computer safely
- Understanding the difference between operating system software and application software
Description of activity with detailed steps
Teacher-led component
- Your teacher may ask you, in small groups, to make a of list all the things a fridge does and a list of all the things you think a computer can do.
- In a group activity your teacher will compile all the group comments in a digital mind map using a concept mapping tool, called Freeplane. She will encourage you to classify the various things the computer will do.
- The teacher will discuss why an operating system is needed and how it works with different applications, for processing your inputs and providing outputs.
- With the help of an image, the teacher will discuss the parts of a computer.
Do you know the parts of a personal computer. (parts numbered in the image above)
- Monitor
- Motherboard
- Central Processing Unit
- Main Memory - Random Access Memory
- Expansion cards
- Power Supply Unit
- Optical Disk Drive
- Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
- Mouse
- Keyboard
Student activities
- In small groups, with teacher guidance, you can switch on a computer and identify the parts you are familiar with
- The teacher will help you create a folder on your computer, for saving your work done in the class.
- With your friends, compare a mobile phone and the computer and list the things each does. Discuss with your friends if there is any difference.
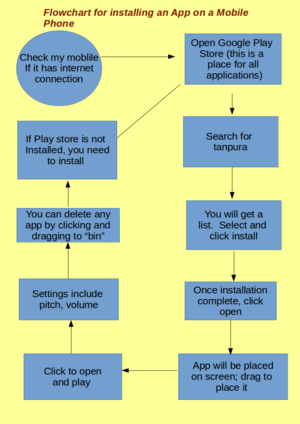
- Develop a flowchart for any activity you have done, or seen someone do. It is better if this is an ICT activity - it can be using the phone, using the computer, playing a video on the TV, etc. See on the side for an example of a flowchart. What you see here is a flowchart for downloading an app on the phone. This has been developed using an application software called LibreOffice Draw, and converted into an image format. You can develop a similar flowchart.
- In groups, you can draw flow charts for the following things (your teacher may discuss additional activities with you):
- Connecting a TV to a cable network
- Using phones to book cooking gas
- Using the farmer SMS service from MKisan portal
- With the help of your teacher, take photographs of the charts and concept maps created, using a cell phone or a digital camera.
Portfolio
We saw earlier that you will keep adding to your digital outputs during this course. You will begin your portfolio collection with the digitized mind maps/ charts.
- Login to the computer (using your personal login, if created or a team login).
- Create a folder with your name in the home folder, and start saving your files.