ICT student textbook/How is a computer different from a fridge
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
How is a computer different from a fridge
What prior skills are assumed
- Academic levels as per class level; no specific ICT skills required
Resources needed
- Working computer lab
- Computer installed with Ubuntu Operating System
- Projection Equipment
- Images to show of the computer
- Handout for Basic digital literacy
- Handout for Freeplane
|
|
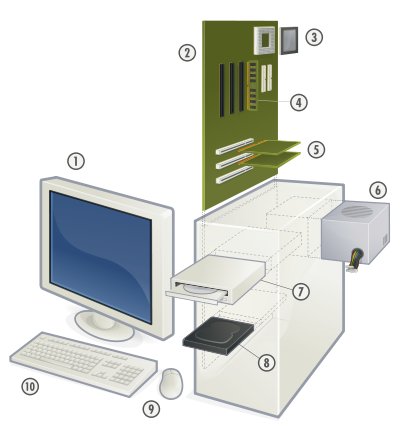
Parts of the computer
- Scanner (nowadays this is in mobile itself, not very much used)
- CPU – This is the processing unit
- Main Memory: RAM: This determines how fast the computer works
- Expansion cards
- Power supply unit
- CD Drive – External storage device
- Hard disk: This determines how much storage capacity
- Motherboard: This is where all instructions are wired together and helps the computer work
- Speakers
- Monitor
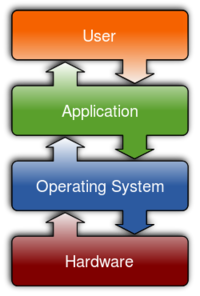
- Operating System
- Application Software
- Keyboard
- Mouse
- External Hard Disk
- Printer
Digital skills
- Getting familiar with an ICT environment and different kinds of ICT devices
- Understanding the difference between operating system softwareb and application software
Description of activity with detailed steps
Teacher-led component
- Your teacher may ask you, in small groups, to make a of list all the items a fridge does and a list of all the things you think a computer can do.
- In a group activity your teacher will compile all the group comments in a digital mind map using a concept mapping tool. She will encourage you to classify the various things the computer will do.
- The teacher will discuss why an operating system needed is and how it works with different applications to ensure that data is communicated between different parts of the computer
- With the help of a schematic the teacher will discuss the parts of a computer
- In small groups, with teacher guidance, you can switch on a computer and identify the parts you are familiar with
- The teacher will help you create a folder on your computer, for saving your work done in the class.
Student activities
- With your friends, compare a mobile phone and the computer and list the things each does
- Discuss with your friends if there is any difference
- For any one mobile application, draw a flowchart to document all the steps in using the application. Click here File:Example flowchart.odg for an example.
- In groups, you can draw concept map for the following things (your teacher will discuss with you additional activities):
- Connecting a TV to a cable network
- Using phones to book cooking gas
- Using the farmer SMS service from MKisan portal
- With the help of your teacher, take photographs of the charts and concept maps created, using a cell phone or a digital camera.
Portfolio
We saw earlier that you will keep adding to your digital outputs during this course. You will begin your portfolio collection with the digitized mind maps/ charts. Create a folder with your name and start saving your files.
