Revision as of 18:10, 17 May 2017
Data can tell stories
In this activity, you will learn see different formats of data and try to interpret the data.
Data can tell stories
Objectives
- Understand that data can be in different formats
- Reading different kinds of data to make meaning
- Analyzing data and expressing
What prior skills are assumed
- Creating folders and saving files
- Opening a given file with the correct application
- Familiarity with using a key board
What resources do you need
- Computer lab with projection
- Access to internet
- Data in the form of bar graphs, pictographs, maps (images)
- Handout for Ubuntu
- Handout for Tux Typing
- Handout for LibreOffice Writer
- Handout for Freeplane
What digital skills will you learn
- Creating and navigating folders (and sub-folders)
- Opening multiple files with multiple applications
- Text entry (local languages)
Description of activity with detailed steps
Teacher led activity
|
|
|
|
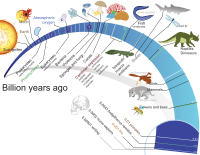
- Look at these examples of data representation with your teacher.
- In small groups, discuss what are the various kinds of analysis you can make from these examples of data.
- For each one your teacher will help you analyze in the form of a concept map.
|
Student activities
- On each of the computers, you will find folders with different data sets.
- Each group of students will get one data set to work with - this will comprise maps, satellite images, pictographs and bar graphs. Your teacher will also give you a set of questions for each data set.
- Make a concept map of what you understand with the data
- You can also add your findings in a text document, using LibreOffice Writer. You can enter text in both Telugu and in English
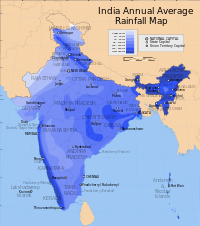
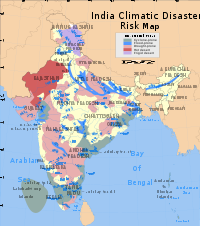
Rainfall
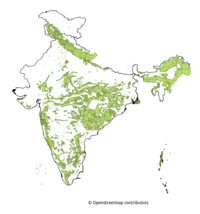
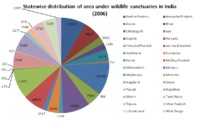
India's forests
Map of Telangana
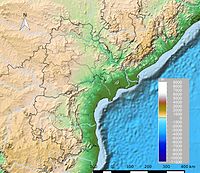
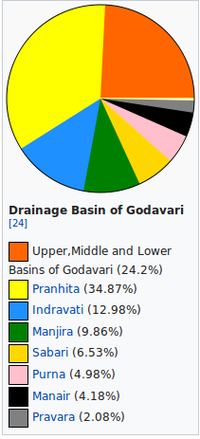
Story of Godavari
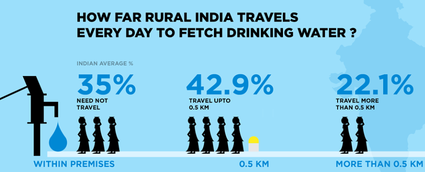
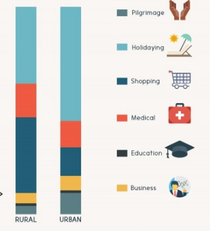
Pictographs-qualitative
Pictographs-quantitative
Portfolio
- Make a concept map, as shown by your teacher, to share your findings:
- What is the data about?
- How was the data represented?
- What was special about each representation?
- What did you conclude from the data?
- Have you studied about this before?
- What more do you want to know?
- For the pictographs, make a concept map to share your understanding of the data you studied.
- Once the concept map has been developed on a paper, with the help of your teacher, digitize it and save it in your folder.