Difference between revisions of "Learn Geogebra"
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 1 Main Window.png|450px]] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 1 Main Window.png|450px]] |
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 2 New point.png|450px]] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 2 New point.png|450px]] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|Step 1 - In GeoGebra you can animate the geometric figure you have drawn and dynamically see how some values like length, area, perimeter of a figure changes, see the same figure in different ways. For detailed resources on how to learn Geogebra you can click on http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Portal:ICT_Literacy. | + | | style="width: 50%;" |Step 1 - In GeoGebra you can animate the geometric figure you have drawn and dynamically see how some values like length, area, perimeter of a figure changes, see the same figure in different ways. For detailed resources on how to learn Geogebra you can click on http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Portal:ICT_Literacy. |
| − | |style="width: 50%;|Step 2 - Drawing points, line segment and rays | + | | style="width: 50%;" |Step 2 - Drawing points, line segment and rays |
Select Point Tool, and click anywhere on the drawing point to plot six points A, B, C, D, E, F. | Select Point Tool, and click anywhere on the drawing point to plot six points A, B, C, D, E, F. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 3 segment between Two points.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_3_segment_between_Two_points.png Image] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 3 segment between Two points.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_3_segment_between_Two_points.png Image] |
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 4 Ray through two points.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_4_Ray_through_two_points.png Image] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 4 Ray through two points.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_4_Ray_through_two_points.png Image] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|Step 3 - | + | | style="width: 50%;" |Step 3 - |
Drawing line segments and lines | Drawing line segments and lines | ||
i. Select Segment between two points tool, click o on point A and then point B. | i. Select Segment between two points tool, click o on point A and then point B. | ||
Select Line through two points tool, click on point C and then point D. | Select Line through two points tool, click on point C and then point D. | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|Step 4 - Select Ray through two points tool, click on point E and the point F. | + | | style="width: 50%;" |Step 4 - Select Ray through two points tool, click on point E and the point F. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 5 Construction of line.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_5_Construction_of_line.png Image] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 5 Construction of line.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_5_Construction_of_line.png Image] |
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 6 Construction a parallel line.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_6_Construction_a_parallel_line.png Image] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 6 Construction a parallel line.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_6_Construction_a_parallel_line.png Image] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|Step 5 - | + | | style="width: 50%;" |Step 5 - |
Can you describe in your own words the difference between a segment, line and ray? Also see the algebra view and observe the equations of the line b and ray c. The line segment a is represented in the algebra view as a = 2.83, where 2.83 is the length of the segment. | Can you describe in your own words the difference between a segment, line and ray? Also see the algebra view and observe the equations of the line b and ray c. The line segment a is represented in the algebra view as a = 2.83, where 2.83 is the length of the segment. | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|Step 6 - ii. Drawing a parallel line | + | | style="width: 50%;" |Step 6 - ii. Drawing a parallel line |
iii. Select Point Tool and click anywhere on the drawing point to plot three points A,B, C. | iii. Select Point Tool and click anywhere on the drawing point to plot three points A,B, C. | ||
iv. Select Line through two points tool, click on point A and then point B. | iv. Select Line through two points tool, click on point A and then point B. | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
Next with Move Graphics view tool and move the drawing pad. Do the two lines ever meet? | Next with Move Graphics view tool and move the drawing pad. Do the two lines ever meet? | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 7 Rotate a ray.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_7_Rotate_a_ray.png Image] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 7 Rotate a ray.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_7_Rotate_a_ray.png Image] |
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 8 Segment with Given Length from Point.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_8_Segment_with_Given_Length_from_Point.png Image] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 8 Segment with Given Length from Point.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_8_Segment_with_Given_Length_from_Point.png Image] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|Step 7 - Rotate a ray | + | | style="width: 50%;" |Step 7 - Rotate a ray |
Draw line segment AB of any length (Segment between two points tool). | Draw line segment AB of any length (Segment between two points tool). | ||
Select the Ray Through two points tool, click on point A, then select another point C on the drawing pad as shown in the figure. | Select the Ray Through two points tool, click on point A, then select another point C on the drawing pad as shown in the figure. | ||
Select the Angle tool, as seen in the figure and click on points B, then A and finally C. You will see an angle measure. Click on the Move tool and move point C. | Select the Angle tool, as seen in the figure and click on points B, then A and finally C. You will see an angle measure. Click on the Move tool and move point C. | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|Step 8 - Start your drawing by using the tool Segment with Given Length from Point. | + | | style="width: 50%;" |Step 8 - Start your drawing by using the tool Segment with Given Length from Point. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 9 Segment with Given Length from Point.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_9_Segment_with_Given_Length_from_Point.png Image] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 9 Segment with Given Length from Point.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_9_Segment_with_Given_Length_from_Point.png Image] |
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 10 perpendicular line through point.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_10_perpendicular_line_through_point.png Image] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 10 perpendicular line through point.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_10_perpendicular_line_through_point.png Image] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|Continue | + | | style="width: 50%;" |Continue |
| − | |style="width: 50%;|Step 10 - Continue by drawing the right angle. Do this by drawing a perpendicular line through point A. Choose the perpendicular line tool, click on point A first and then on the line. | + | | style="width: 50%;" |Step 10 - Continue by drawing the right angle. Do this by drawing a perpendicular line through point A. Choose the perpendicular line tool, click on point A first and then on the line. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 11 perpendicular line through point A.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_11_perpendicular_line_through_point_A.png Image] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 11 perpendicular line through point A.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_11_perpendicular_line_through_point_A.png Image] |
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 12 Circle with Center and Radius.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_12_Circle_with_Center_and_Radius.png Image] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 12 Circle with Center and Radius.png|450px]] [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geogebra_12_Circle_with_Center_and_Radius.png Image] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;| Continue | + | | style="width: 50%;" | Continue |
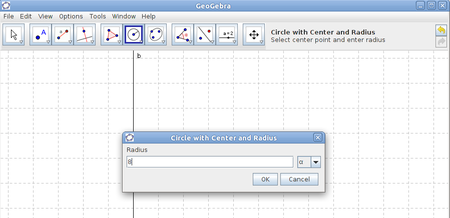
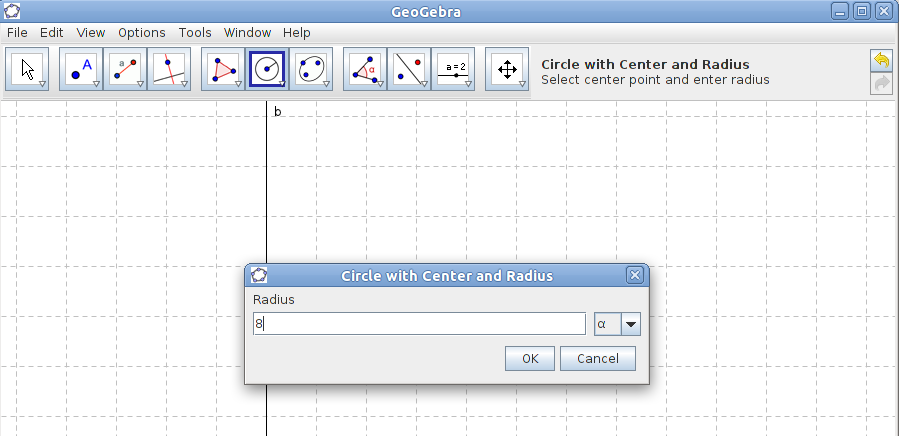
| − | |style="width: 50%;|Step 11- To mark the third corner of the triangle you use one of the circle tools, Circle with Centre and Radius. | + | | style="width: 50%;" |Step 11- To mark the third corner of the triangle you use one of the circle tools, Circle with Centre and Radius. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 13 Numbers of Radius.png|450px]] [[File:Geogebra_13_Numbers_of_Radius.png]] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 13 Numbers of Radius.png|450px]] [[File:Geogebra_13_Numbers_of_Radius.png]] |
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 14 Intersect Two Objects.png|450px]] [[File:Geogebra_14_Intersect_Two_Objects.png]] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 14 Intersect Two Objects.png|450px]] [[File:Geogebra_14_Intersect_Two_Objects.png]] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|Step 12 - Click on the point B and fill in the length of the hypotenuse as radius. | + | | style="width: 50%;" |Step 12 - Click on the point B and fill in the length of the hypotenuse as radius. |
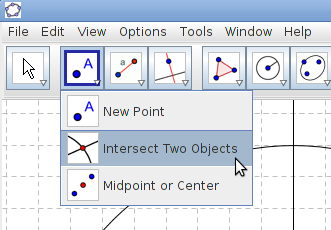
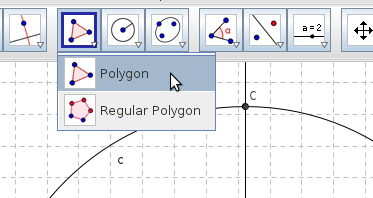
| − | |style="width: 50%;|Step 13 - Choose the tool Intersect Two Objects, click on the circle and the perpendicular line. The point in the intersection is the third corner of the triangle. | + | | style="width: 50%;" |Step 13 - Choose the tool Intersect Two Objects, click on the circle and the perpendicular line. The point in the intersection is the third corner of the triangle. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 15 Polygon.png|450px]] [[File:Geogebra_15_Polygon.png]] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 15 Polygon.png|450px]] [[File:Geogebra_15_Polygon.png]] |
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 16 Show Object.png|450px]] [[File:Geogebra_16_Show_Object.png]] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 16 Show Object.png|450px]] [[File:Geogebra_16_Show_Object.png]] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|Continue | + | | style="width: 50%;" |Continue |
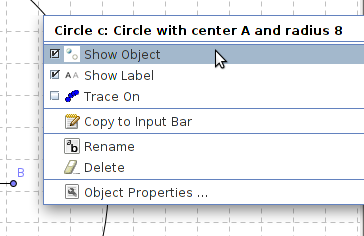
| − | |style="width: 50%;|Step 15 - The perpendicular line and the circle, even the points do not need to be visible or seen now, you only want to show the triangle. Hide an object by right-clicking the object and uncheck Show Object by clicking on it. | + | | style="width: 50%;" |Step 15 - The perpendicular line and the circle, even the points do not need to be visible or seen now, you only want to show the triangle. Hide an object by right-clicking the object and uncheck Show Object by clicking on it. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 17 Show Label.png|450px]] [[File:Geogebra_17_Show_Label.png]] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 17 Show Label.png|450px]] [[File:Geogebra_17_Show_Label.png]] |
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 18 Object Properties.png|450px]] [[File:Geogebra_18_Object_Properties.png]] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 18 Object Properties.png|450px]] [[File:Geogebra_18_Object_Properties.png]] |
|- | |- | ||
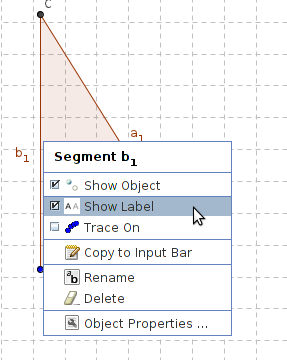
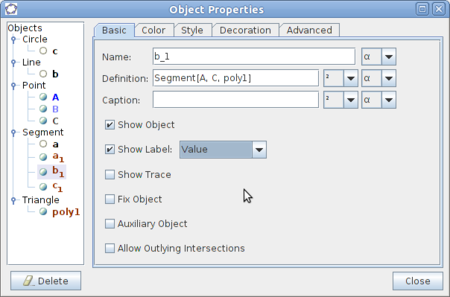
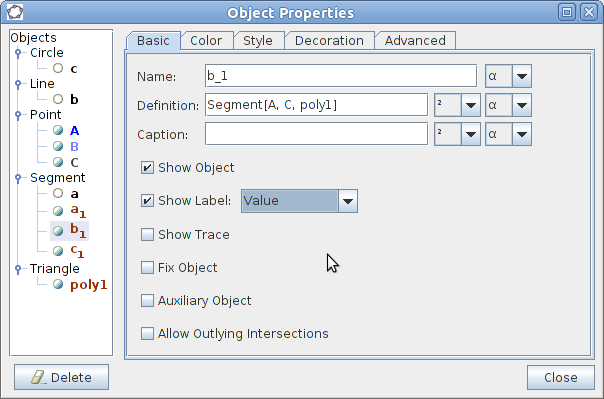
| − | |style="width: 50%;|Step 16 - The lengths of the sides in the triangle can be shown. Right-click one of the sides and choose Object Properties in the menu which shows up. Check the Show Label field and choose Value from the drop down list. | + | | style="width: 50%;" |Step 16 - The lengths of the sides in the triangle can be shown. Right-click one of the sides and choose Object Properties in the menu which shows up. Check the Show Label field and choose Value from the drop down list. |
| − | |style="width: 50%;|Continue | + | | style="width: 50%;" |Continue |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 19 Area of the angle.png|450px]] [[File:Geogebra_19_Area_of_the_angle.png]] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 19 Area of the angle.png|450px]] [[File:Geogebra_19_Area_of_the_angle.png]] |
| − | |style="width: 50%;|[[File:Geogebra 20 Angle Moving.png|450px]] [[Geogebra_20_Angle_Moving.png Image]] | + | | style="width: 50%;" |[[File:Geogebra 20 Angle Moving.png|450px]] [[Geogebra_20_Angle_Moving.png Image]] |
|- | |- | ||
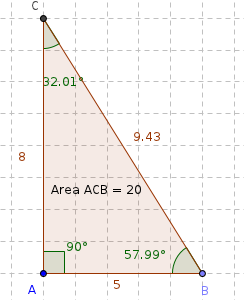
| − | |style="width: 50%;|Step 17 - To show the size of the angles use the Angle tool. Click on each vertex of the triangle. The order in which you click the vertices must be in the clock wise direction. In this figure click in this order BAC, CBA, and ACB. | + | | style="width: 50%;" |Step 17 - To show the size of the angles use the Angle tool. Click on each vertex of the triangle. The order in which you click the vertices must be in the clock wise direction. In this figure click in this order BAC, CBA, and ACB. |
| − | |style="width: 50%;|Step 18 - Click on Area tool and then click on the polygon. <br> | + | | style="width: 50%;" |Step 18 - Click on Area tool and then click on the polygon. <br> |
Change the shape of the triangle by moving the points you are able to move (use the Move tool). | Change the shape of the triangle by moving the points you are able to move (use the Move tool). | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 133: | Line 133: | ||
=The application on mobiles and tablets= | =The application on mobiles and tablets= | ||
| − | Geogebra can also be downloaded for the mobile from Google Playstore | + | Geogebra can also be downloaded for the mobile from [https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=org.geogebra.android&utm_source=Download%20page&utm_medium=Website&utm_campaign=Android%20App%20for%20Phones Google Playstore]. |
=Ideas for resource creation= | =Ideas for resource creation= | ||
Revision as of 12:12, 20 February 2017
Introduction
Geogebra is an interactive geometry , algebra, statistics and calculus application, intended for learning and teaching mathematics from primary school to university level. Geogebra’s tools enable us to produce new objects using pointing device. They can be activated by clicking on the corresponding buttons of the Toolbar. This application is free and licensed under the GNU Public License.
ICT Competency
Educational application and relevance
Geogebra is an outstanding technology tool that improves mathematics education.Through simulations, students create concrete representations of geometric theorems instead of abstractly configuring images in the mind. Geogebra is an exciting, Web based application that eliminates concept of memorization. In addition to this, students transform from passive classroom observers to active, excited participants. Meaningful learning occurs as the students manipulate and test data with-in the Geogebra.
Version
The GEOGEBRA version - 5.0.236.0-3D…..
Geogebra is part of the Ubuntu distribution (in the training). This can be opened from Applications → Education → Geogebra.
Configuration
There is no specific configuration for this tool or application.
Overview of Features
The tool has several features...like….,
- We can create special .ggb files which can be used to apply a style to other files.
- We can load a .ggb file into another.
- Opacity for lines and perimeters of shapes.
- Insert image tools now supports SVG files.
- This is a simulation as well as graphic plotter
Other similar applications
Development and community help
Working with the application
Functionalities
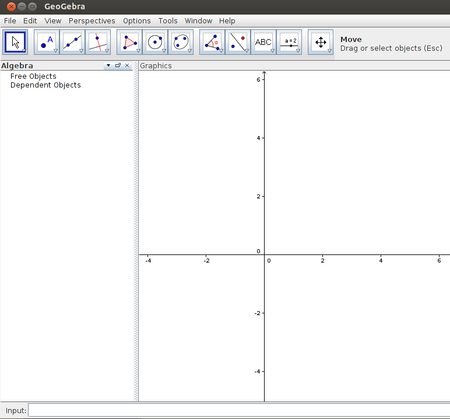
|
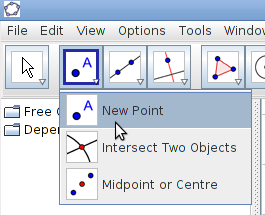
|
| Step 1 - In GeoGebra you can animate the geometric figure you have drawn and dynamically see how some values like length, area, perimeter of a figure changes, see the same figure in different ways. For detailed resources on how to learn Geogebra you can click on http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Portal:ICT_Literacy. | Step 2 - Drawing points, line segment and rays
Select Point Tool, and click anywhere on the drawing point to plot six points A, B, C, D, E, F. |
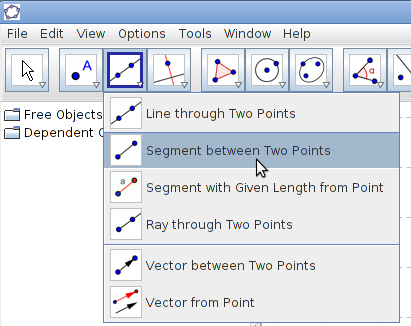 Image Image
|
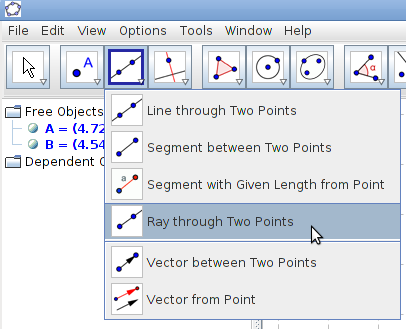 Image Image
|
| Step 3 -
Drawing line segments and lines i. Select Segment between two points tool, click o on point A and then point B. Select Line through two points tool, click on point C and then point D. |
Step 4 - Select Ray through two points tool, click on point E and the point F. |
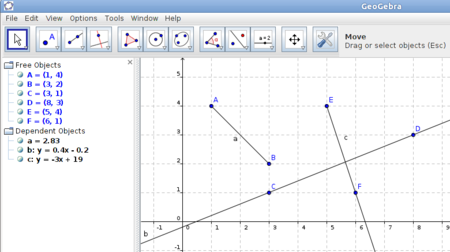 Image Image
|
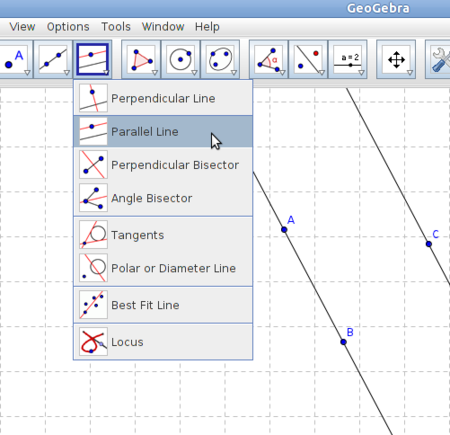 Image Image
|
| Step 5 -
Can you describe in your own words the difference between a segment, line and ray? Also see the algebra view and observe the equations of the line b and ray c. The line segment a is represented in the algebra view as a = 2.83, where 2.83 is the length of the segment. |
Step 6 - ii. Drawing a parallel line
iii. Select Point Tool and click anywhere on the drawing point to plot three points A,B, C. iv. Select Line through two points tool, click on point A and then point B. v. Select Parallel Line tool, click on point C first. Then click on line AB. Now use the Move Tool and move points A, B and C. What do you observe? Describe it. Next with Move Graphics view tool and move the drawing pad. Do the two lines ever meet? |
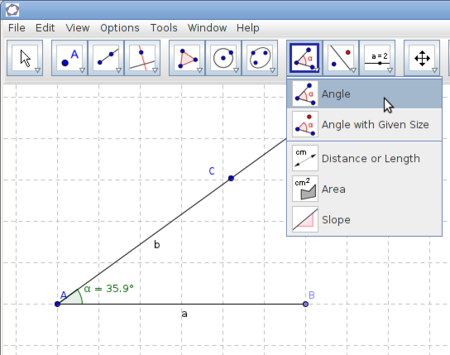 Image Image
|
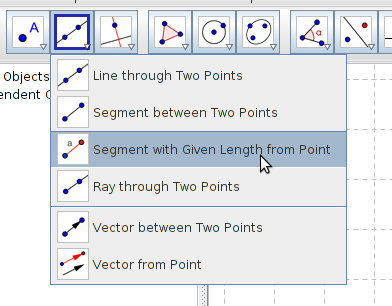 Image Image
|
| Step 7 - Rotate a ray
Draw line segment AB of any length (Segment between two points tool). Select the Ray Through two points tool, click on point A, then select another point C on the drawing pad as shown in the figure. Select the Angle tool, as seen in the figure and click on points B, then A and finally C. You will see an angle measure. Click on the Move tool and move point C. |
Step 8 - Start your drawing by using the tool Segment with Given Length from Point. |
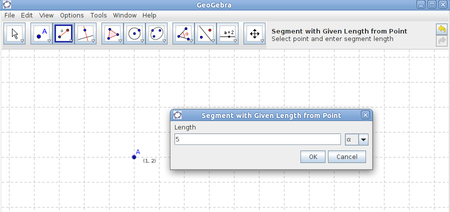 Image Image
|
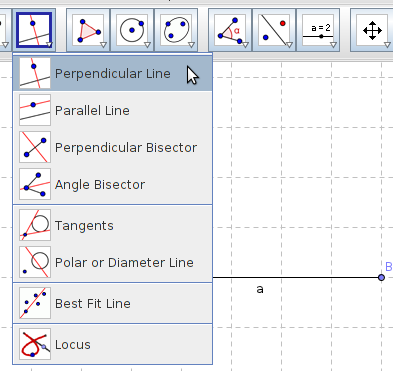 Image Image
|
| Continue | Step 10 - Continue by drawing the right angle. Do this by drawing a perpendicular line through point A. Choose the perpendicular line tool, click on point A first and then on the line. |
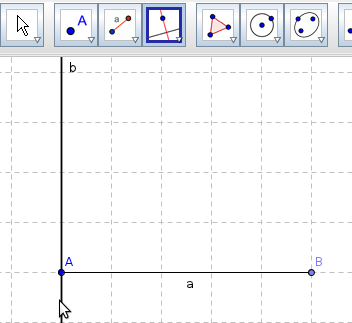 Image Image
|
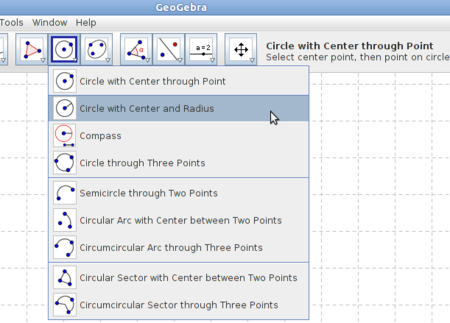 Image Image
|
| Continue | Step 11- To mark the third corner of the triangle you use one of the circle tools, Circle with Centre and Radius. |
|
|
| Step 12 - Click on the point B and fill in the length of the hypotenuse as radius. | Step 13 - Choose the tool Intersect Two Objects, click on the circle and the perpendicular line. The point in the intersection is the third corner of the triangle. |
|
|
| Continue | Step 15 - The perpendicular line and the circle, even the points do not need to be visible or seen now, you only want to show the triangle. Hide an object by right-clicking the object and uncheck Show Object by clicking on it. |
|
|
| Step 16 - The lengths of the sides in the triangle can be shown. Right-click one of the sides and choose Object Properties in the menu which shows up. Check the Show Label field and choose Value from the drop down list. | Continue |
|
 Geogebra_20_Angle_Moving.png Image Geogebra_20_Angle_Moving.png Image
|
| Step 17 - To show the size of the angles use the Angle tool. Click on each vertex of the triangle. The order in which you click the vertices must be in the clock wise direction. In this figure click in this order BAC, CBA, and ACB. | Step 18 - Click on Area tool and then click on the polygon. Change the shape of the triangle by moving the points you are able to move (use the Move tool). |
File formats for creation
Saving the file
Click File > Save to save the file. It will be saved in .ggb file.
Export and publishing files
Advanced features
Installation
| Method of installation | Steps |
|---|---|
| From Ubuntu software Centre | Steps - Applications → Ubuntu soft-ware center → search Geogebra → Install. |
| From Terminal | Steps - Applications → Accessories → Terminal.
Open terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T) and then type below command “sudo apt-get install geogebra” Press Enter key and it will ask your Ubuntu password, type your ubuntu password and then press “Enter”. It will will show how space it will from storage space and some other details, again press “Enter” key. |
| From the web | Steps - Web download , Web based registation |
| Web based registration | Steps |
The application on mobiles and tablets
Geogebra can also be downloaded for the mobile from Google Playstore.
Ideas for resource creation
References
How to use template
{{subst:Explore_an_application}} on the page you create for your tool. Page Name should be "Learn ToolName"
