ICT student textbook/Science Technology and Society
Science and technology
Many times you hear the word science and technology together. What is the connection between the two? Do you know? Study of science includes a method of observing things around us, thinking about why those events happen, explaining why the events happen, recording information about the events and also predicting what might happen. Often, scientists imagine what might be the solution and what might be the answer to the puzzles around us. The understanding of phenomena can lead to the development of tools – this is what we call technology. The technology can provide us more methods of observing, experimenting and recording. And this in turn results in the advancement of science. Thus, science and technology share a symbiotic relationship.
| A symbiotic relationship is when two phenomena work together and one affects the other. This term originated in biology and ecology to describe interactions between different organisms.
Watch the attached video for examples of symbiotic relationship. |
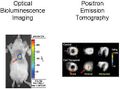
Can you think of examples of where technology has helped the growth of science? One area is that of cell biology. Until the microscope was invented by Robert Hooke and Anthony Leeuwenhoek, the study of cells was not possible. Now we study structure of cells, growth of cells, disease-affected cells, cell reproduction, gene sequencing and DNA using many advanced microscopes, cameras; the data and images are analysed using computers.
As you can see the microscope started with simple magnification; now,the images captured by the microscope and camera can be input into the computer for further study and research. It has even become possible to scan parts of the body for diagnosing illnesses. Many complex problems in biology are being studied through the use of computers. Some of these areas include cancer research, study of how certain diseases develop and development of medicines.
Similarly, our understanding of astronomy has been expanded after the invention of the telescope. But to make a telescope or microscope, we need to understand the properties of light. We must understand how a lens works, how light travels. Thus, science and technology are very closely connected.
Your teacher will discuss with you more examples of how technology has impacted the way we understand many natural phenomena.
Information and communication technologies (ICTs)
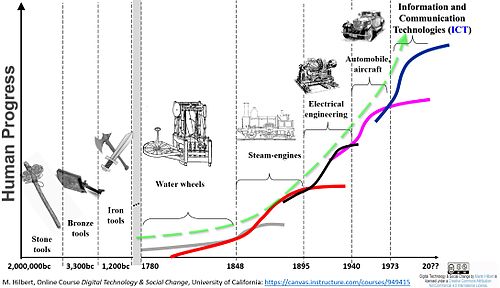
Information is not new for human beings; communication has been known since the time human beings lived in caves. Thus ICT are as old as human beings themselves; human beings needed to communicate with one another, beginning with symbolic (non verbal) ways, before language was invented. The language we speak could be seen as first 'ICT', it enabled (oral) communication amongst human beings. Writing and script was the next technological advancement - around 5000 years ago - which enabled information could be created and communicated at different times and in a different place. Oral communication does not have this benefit, Writing also enabled easier recording of human history and thus the invention of script was a landmark in the history of ICTs. Next came printing which made it possible replicate writing. The invention of radio and television was the next advancement in ICT as it became possible for more and more people to access information.
Thus, the technology for information creation and communication has been changing, connected with the advancements in scientific knowledge. Changes happened in the way computing evolved and changes happened in the way communication technology evolved, each impacting the other to produce the ICT environment we are now in; and which is still changing rapidly.
Analog and digital technologies
Impact on computing and development of computers
| During the mechanical and electric analog phases of technology, information was created by a series of physical changes converted into electrical impulses for storing and machine, and each analog information storage required a specialized equipment to decode and read the information. A cassette player or a gramaphone disc is an example of such a device. Analog machines could be programmed for specific applications as well as for generalized computation. Representing information for computing using physical changes often meant that the results could not be accurate as the changes could not be replicated exactly. | See below how a difference engine, designed by Charles Babbage worked.
|
| An important breakthrough came when the binary system was invented. In the binary system information can in a series of "0"s and "1"s thus allowing information to be accessed through only a combination of "1"s and "0"s. This allowed information to be communicated in discrete bits which could be combined and recombined. Such a computer which uses "0"s and "1"s to perform computations a digital computer. What makes our society now different from ever before is the presence of digital technologies. Combined with the development of new methods of designing circuits like transistors and micro chips, it became possible to design computers which performed computations using digital methods. This improved the reliability and ease of computations significantly over the analog machines. The digital electronics changed operations in many applications including manufacturing, however the impact on ICT has been almost revolutionary. This has led to the growth of computers as we know it - from large clunky computers to the computer on your desktop to the laptop and now the smart phone. | slideshow - http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/computers/
See the slideshow here for a glimpse of how the digital technology revolutionized history of computing. |
Impact on communication technologies
What is the word that comes to your mind when you say communication? The phone, precisely the cell phone. We will now look at how the communication technologies evolved.
Radio communication
The earliest electronic communication devices functioned using radio technology. Many communication devices we know today also function through radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves. They carry energy through repeated propagation of electric and magnetic fields. Radio waves carry a certain amount of energy and can travel over large distances. When the wave reaches the destination, the receiver gets the amount of information. We cannot see radio waves but we can detect them by building receivers that can detect them. These are called as antennae. They scan the environment for radio signals and respond when they find a signal. They detect the radio signal by the effect of the changing electrical and magnetic fields. Frequency gives a measure of how fast the radio wave is being produced and depends on the source from where the radio waves start. Different radio waves come at different frequencies and we need to build transmitters that detect them. Sound is a pressure wave – when we produce a sound it travels by disturbing the air particles. If there is no medium, sound cannot travel. What happens when we hear something on a radio? Originally sound is produced and then it converted into radio waves. These waves are sent and received through instruments called antennae. When your radio antennae receives this radio wave, this is converted back into sound and is played.
Use of radio waves in astronomy : Radio waves are also produced by many celestial objects. By detecting the radio waves that travel through the atmosphere, it is possible to construct images of the astronomical objects. Radio waves can pass through dust and gas unlike light. Radio astronomy along with optical observation is allowing us to understand the universe better.
Telephone
Before the cell phone came, most of the long distance voice communication was through the regular telephone. This was based on the idea of travelling sound waves. They cause the mouthpiece to vibrate and this vibration is carried to the receiver at the other end. When a call came from one number, there will be an operator who sits at an office who will connect the call to another receiving number. Now this is different with automatic switches which connect the calls. The transmission of the signals has also become different now with voice being converted into electrical signals. All these transmissions used to happen through physical cables. These cables were either made of copper or optical fibres.
When you make a phone call, the voice signals from your phone get transmitted through these fibres to the nearest telephone exchange and through a series of switches sent to the receiver. Usually the first few numbers in our telephone number indicates the exchange information. In the earlier days, long distance calls (outside of the local exchange) could only be made by booking a trunk call. The users had to 'book' or rent the line through which the call can be made and this used to be done manually by the telephone operators in the exchange. Now-a-days, with automatic switches, long distance calls can be made directly to any number, even outside the country.
The cell phone
The telephone and the radio came together - And we call that the cell phone! We saw how a telephone works. We also saw what radio waves are and we have some idea of what frequencies mean. There are many frequencies available for the users to talk on. Any geographic area is divided into small plots, and in each area a fixed number of frequencies is used. Each of these areas are called cells. The cell phone is called a cell phone because it functions by dividing a geographical area into small plots or cells through which the transmission takes place. It is possible to make and receive calls when there is a cell phone tower near your area for receiving and sending that frequency. Now do you understand what we mean when we say 'my cell phone has no coverage here'? It is because of this also that cell phones sometimes do not work inside buildings when the radio signals are disturbed. Just like an exchange for regular telephone calls, there is a mobile switching that allows you to make calls even when you move from one cell to another!
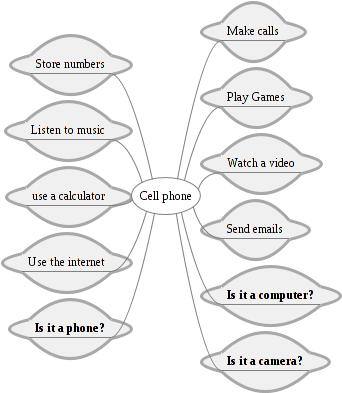
Can you make a list of all the things a cell phone does?
What can ICT do
ICT have changed the society
Look around you - can you make a list of things that have digital technologies involved in them? Yes, that is right. Starting from the computer in your school, television, movies, videos and other materials for subject learning mobile communication, Aadhar card, land records, bank accounts, pension accounts and so many more things, ICT have become integrated into society in many ways.
1. ICT can help create
ICT can create information in so many different ways - maps, audio, video, text, numeric data. Expressing yourself and creating materials is not limited only to text. This means newer and newer methods of knowledge creation and sharing. You can learn in different ways. How we learn and what is needed to be learnt have become different. For example, we no longer need to learn about a withdrawal slip, we need to know how to use the ATM. Your teacher can now take a video of a class in your school and share it. There is a great convergence of many technologies that is happening, a mobile is approaching the computer, the internet taking over.
2. ICT can help connect and communicate
The most important thing about ICT today is the internet. The internet has changed the way we think of communicating. Talking to a friend through whatsapp or telegram chats, emailing or making a video call are just some of the ways in which the internet has changed the way we interact with each other in society. With the internet, you can connect to any computer in the world and access information.
ICT have brought together people, If so many things are impacted by ICT, it is important to understand how these work, and how they should be used ethically and safely. Technology should be treated like a common resource where everyone can access it, interact with it, benefit from it and contribute to it. It should be used such that more and more people can get access in society should be treated like a public information good.