Difference between revisions of "Explore a computer"
m (1 revision imported: from troer) |
Revision as of 13:58, 28 June 2017
ICT refer to an entire range of devices that use digital methods to process represent and communicate information. The desktop computer, laptop, tablet and the smart phone are all ICT devices. Let us explore below the parts of a desktop computer.
Parts of a computer
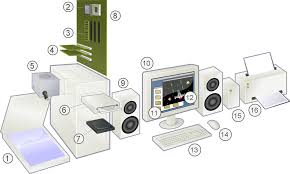
| 1. Scanner (nowadays scanning function is available in the mobile phone, hence a separate scanner is not often used) | 2. CPU (Central Processing Unit): does the processing work of the computer. It contains “chips” which determine the speed of computer. For example i5 is a chip manufactured by Intel. |
| 3. RAM (Random Access Memory): This is the storage space in the computer. Temporally it will store frequently used applications and data in it, to increase the speed of the computer. The size of RAM determines how fast the computer works | 4. Expansion cards. |
| 5. Power supply unit, which supplies power to the computer. | 6. CD Drive – External storage device. This is now becoming obsolete as USB storage devices / 'pen drives' are becoming more popular |
| 7. Hard disk: Hard disk stores the user data as well as the software. This storage capacity of the computer is specified in terms of GB (Gigabytes), 1 GB = 109 bytes or 1000,000,000 bytes | 8. Motherboard: This is where all instructions are wired together and helps the computer work |
| 9. Speakers, these amplify any audio played on the computer | 10. Monitor, for displaying our instructions to the computer and its responses. Monitor consumes quite a bit of electricity, so should be kept in the 'off' mode when the computer is not being actively used |
| 11. Operating System. An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs. All computer programs (application software) require an operating system to function. | 12. Application Software - An application program (app or application for short) is a computer program designed to perform a group of activities. Examples of an application include a text editor, a spreadsheet, a web browser, or a photo editor. The collective noun application software refers to all applications collectively |
| 13. Keyboard, similar to a type writer keyboard. It is an input device, used for typing instructions (text, numbers, special characters) to the computer. | 14. Mouse, another input device, that works on the Graphical User Interface of the computer |
| 15. External Hard Disk, additional storage space. | 16. Printer, output device |
Hardware: Parts 2-8, 10, 13 and 14 constitute basic hardware and are parts of all computing devices. These have now all been combined into one unit in a laptop or mobile. Largely, the hardware is divided into input devices and output devices and storage functions.
| Input Devices | Output Devices |
|---|---|
| Mouse | Monitor |
| Keyboard | Projector |
| Microphone | Printer |
| Scanner | Speakers |
| Web cam |
Using the keyboard
The keyboard is usually the main device to providing instructions to the computer. The keys on the keyboard can be divided into several groups based on function:
- Typing (alphabets and numbers) keys: These keys are arranged as in a traditional 'QWERTY' typewriter
- Special purpose keys: These keys are used alone or in combination with other keys to perform certain actions, such as CTRL, ALT, ESC, Function keys etc.
- Navigation keys: These keys are used for moving around in documents / editing text. They include the arrow keys, HOME, END, PAGE UP, PAGE DOWN, DELETE and INSERT.
- Numeric keypad: The numeric keypad is handy for entering numbers quickly. The keys are grouped together in a block like a conventional calculator or adding machine.
Special typing keys
SHIFT: Press shift in combination with a letter to type an uppercase letter. Press shift in combination with another key to type the symbol shown on the upper part of that key.
ENTER: Press enter to move the cursor to the beginning of the next line.
SPACEBAR: Press the spacebar to move the cursor one space forward.
BACKSPACE: Press backspace to delete the character before the cursor or the selected text.
ALT: Activates the menu of the application. Can be used along with arrow keys to select applications
The navigation keys allow you to move the cursor, move around in documents and edit text. The following table lists some common functions of these keys.
LEFT ARROW, RIGHT ARROW, UP ARROW or DOWN ARROW : Move the cursor or selection one space or line in the direction of the arrow.
HOME : Move the cursor to the beginning of a line.
END: Move the cursor to the end of a line.
CTRL+HOME: Move to the top of a document.
CTRL+END: Move to the bottom of a document.
PAGE UP: Move the cursor or page up one screen.
PAGE DOWN: Move the cursor or page down one screen.
DELETE: Delete the character after the cursor, or the selected text; in Windows, delete the selected item and move it to the Recycle Bin.
INSERT: Turn insert mode off or on. When insert mode is on, text that you type is inserted at the cursor. When insert mode is off, text that you type replaces existing characters.
| Storage devices |
|---|
| External HDDs |
| Pendrives |
| DVD/CD |
Internet connectivity devices: A modem is used for connecting the computer- laptop or mobile to the internet, through a broadband connection. In a networked environment, this modem will be used together with a Local Area Network (LAN). Your school ICT Lab should be configured as a LAN, to get the benefits of local networking, such as sharing data (files) and services (printing etc).
Peripherals: Speakers, external hard disk and printers are important peripherals that are used for storing and output and these can be connected to the computer or laptop.
Safely operating a computer
Nowadays computer usage is increased all over the world. Safely using and maintaining computer/computers lab is very important. Safely operating the computer involves both the hardware and software.
Hardware Safety
1. A proper electrical circuit and good quality wiring is essential for the physical safety of the computer as well as the user's safety.
- Make sure electric earthing is done properly
- Always run your computer on a UPS as this will help protect it from electric surges.
- If you don't have UPS at least use a spike protector. It will protect against power surges. This is essential, especially if using a desktop computer.
2. Computer lab or room should always be clean without dust.
- Clean the floor regularly
- Clean the computers by using dry cloths
- Remove the non-working computers or peripherals from the lab to avoid dust.
3. If you are going to open the CPU cabinet, do so only after powering off the computer.
4. Never have liquids or solids near a computer you are working on.
5. Be careful when plugging in USB, ethernet, speakers, printer etc. into your computer. Ports such as USB and Ethernet can easily be damaged from careless placement. These repairs can be costly and these ports are a necessity.
6. Don’t leave the computer without shutting down it, after your work completes.
Software Safety
Nowadays we are using many applications software in our works and many times we will install applications without knowing about it. This is the main cause to damage our computer software regularly.
1. Before installing any applications in your computer, you should know about its functionality and use.If you are not sure about it please contact the concern person and do it.
2. Make sure you know what you are doing while dealing with the software of your computer.
3. Regularly take back of your computer - at least once in a three months.
4. Remove the unwanted software which installed in your computer.
5. If the computer is used by multi users, create separate login account for each of them.
5. If your computers is using by multiple users, don't share the administration password with all of them.
6. Use the firewall to protect internet misuse from the users.
7. Always need to shut down the computers from the software.
8. Keep updating your computer software and application software for better performance.
Different Computer ports
A computer port is also called as a Communication Port as it is responsible for communication between the computer and its peripheral device. There are two kinds of ports - Male port and Female port. The female port has the necessary indentations for the male port to be connected. The images below describe the two kinds of ports.
- Male and female ports
Here we will give brief introduction to different types of ports along with their applications.
- USB Port :USB is an abbreviation of Universal Serial Bus. The USB port is the most widely used port. The USB lets you to connect several types of devices to your laptop or computers such as external hard drives, pen drives, USB modem, cameras, keyboard, mice etc. It also helps in charging mobile phones and such small devices as it supplies small amount of power the connected devices. When the standard USB version 2.0 offers a transfer speed of 480 Mbps, the latest version 3.0 offers higher speed of 5Gbps.
- Network Port or RJ 45/Ethernet Port: This port is basically use it for connecting internet through LAN cable.
- Audio Port : It is the most commonly found audio port that can be used to connect Headphones, mic and external speakers.
- Memory Card Reader: This port is available only in Laptops. which is pretty common on modern day laptops as it allows you to insert any kind of memory card into your system.This way you can avoid connecting USB cables to transfer the files.
- VGA port : is an abbreviation of Video Graphics Array. This is used to connect your system to any analog monitor, LCD TV and projectors.Nowadays VGA ports are gradually being replaced by HDMI port.
- HDMI port : HDMI is an abbreviation of High Definition Media Interface.HDMI is a digital interface to connect High Definition and Ultra High Definition devices like Computer HD monitors, HDTVs, Blu-Ray players, High Definition Cameras etc. All old laptops or computers will not have this HDMI port.