Difference between revisions of "Learn Thunderbird"
m (1 revision imported: from troer) |
Revision as of 13:57, 28 June 2017
Introduction
Email (or simply mail) is a digital equivalent of sending a letter to a person. Just like a letter is written to a person, for a purpose, an email is also sent to another person (or persons, or a group of persons). Email requires Internet connectivity, checking web-mail (logging into on-line email) requires continuous connectivity. However, in many situations, we do not have internet connectivity. If we use a ‘email client’ then emails can be ‘downloaded’ to your computer, in which case they can be read and processed even when there is no connectivity. Mozilla Thunderbird is a popular email client. Secondly, if you have more than one email account, you can configure all of them in Thunderbird, so that you can read all your mails in one place. We will assume that you are familiar with using email features such as: 1. Composing and sending a mail. Replying to and forwarding a mail. Deleting unwanted mails 2. Creating folders for storing mails (classification of mails by topic or by sender or by yea
ICT Competency
Connecting and learning
Educational application and relevance
Thunderbird is an email client. It will help teachers and students to share information and resources with one another. The emails in thunderbird are like a library, since emails (and resources) can be categorized and stored and searched and retrieved later.
Version
Thunderbird Version 45.2.0 on Ubuntu GNU/Linux
Configuration
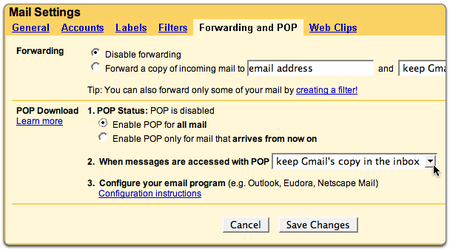
Thunderbird needs to be configured on your computer, by providing the email account, incoming and outgoing server information to your computer. Any paid email provider will give you this information. Free (mufta) email provider such as gmail also provides this information. In our illustration below, we will take gmail (from google) for configuring on Thunderbird on your computer.
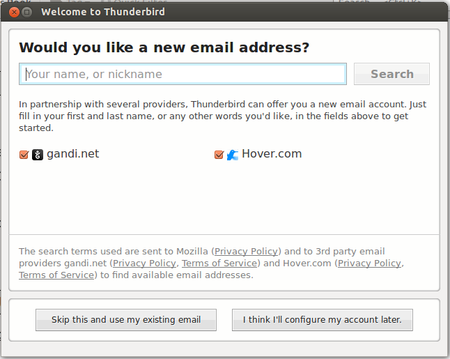
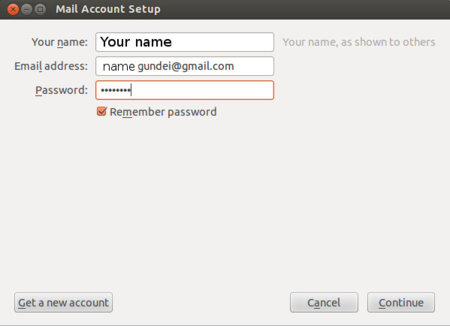
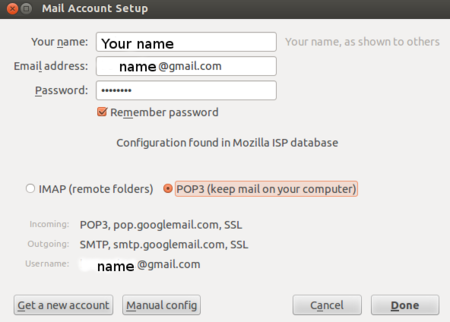
Configuration of Thunderbird on your computer can be done in two parts. 1. Configuring your gmail to allow mail download to your computer / mail client 2. Configuring your Thunderbird mail client, this consists of four steps
Overview of Features
Thunderbird is an email client, which does the usual functions of mailing – receiving, sending and storing emails. Mails can be stored in folders and sub folders to categorize mails based on subjects or senders or time periods or a combination of these. Files can be attached and shared with others. Emails can be searched easily by providing information on different elements such as sender, receiver, date etc. Mail ids can be connected to form ‘mailing-lists’ (such as google groups), by which, mail sent to the list id will be sent to all members of the group, this is ideal to create ‘professional learning communities’ of teachers with a common interest or need.
Other similar applications
Other free email clients include Evolution, Kmail, Claws mail etc. Microsoft Outlook is a proprietary email client, so is gmail.
Development and community help
1. User manual for Thunderbird is available on http://support.live.mozillamessaging.com/en-US/thunderbird/20160711140201
2. Community forum is at https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/get-community-support
3. Official Website
Working with the application
Functionalities
File formats for creation
Not Aplicable
Saving the file
In Thunderbird, each mail is stored as a file with a .eml extension
Export and publishing files
A mail can also be printed or exported to PDF. You can also create an image file from Thunderbird through the using the screenshot application.
Advanced features
Installation
1 From Software center -Type Thunderbird in search bar and then click install
2 From terminal
sudo apt-get install thunderbird
3 Web download - Click here to download it from website
4 Web based registration
The application on mobiles and tablets
Thunderbird is not available on mobiles and tablets. There are apps available for Android, for downloading and processing email, such as K-9 mail
Ideas for resource creation
Thunderbird is a tool for connecting, not for creating.
References
[ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mozilla_Thunderbird wikipedia]