Difference between revisions of "ICT teacher handbook/ICT for subject specific resource creation"
m |
m |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
=== Subject based free and open educational applications === | === Subject based free and open educational applications === | ||
The Free and Open Source Software community has developed hundreds of educational applications, which teachers can use to teach their subjects. These tools complement and supplement the traditional teaching methods that teachers use, such as lecture, chalk and talk, group discussions, projects etc. These tools have a few potential advantages: | The Free and Open Source Software community has developed hundreds of educational applications, which teachers can use to teach their subjects. These tools complement and supplement the traditional teaching methods that teachers use, such as lecture, chalk and talk, group discussions, projects etc. These tools have a few potential advantages: | ||
| − | # Many of them are interactive and allow for the learner to provide inputs and get feedback/responses and create resources / digital artefacts. This can support a constructivist approach. | + | # Many of them are interactive and allow for the learner to provide inputs and get feedback/responses and create resources / digital artefacts. This can support a constructivist approach. One of [[wikipedia:Jean_Piaget|Piaget]]'s contemporaries, [[wikipedia:Seymour_Papert|Seymour Papert]] conceptualised this process as '[[wikipedia:Constructionism|Constructionism]]' |
# Resources created by the learner can be assessed by the teacher for conceptual understanding | # Resources created by the learner can be assessed by the teacher for conceptual understanding | ||
# Peer learning possibilities amongst learners can be supported by encouraging group learning (this can take advantage of the limited ICT resources that may be available in the school, due to which a 2:1 or even 3:1 learner:computer ratio may be required) | # Peer learning possibilities amongst learners can be supported by encouraging group learning (this can take advantage of the limited ICT resources that may be available in the school, due to which a 2:1 or even 3:1 learner:computer ratio may be required) | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
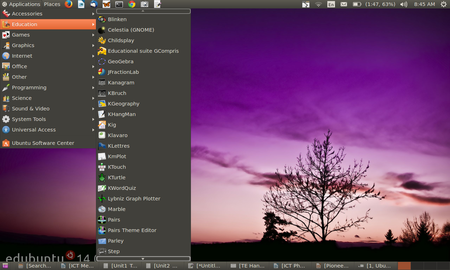
[[File:Edubuntu_Education_Menu.png|450px]] | [[File:Edubuntu_Education_Menu.png|450px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | More educational applications can be downloaded from the Ubuntu Software Centre, internet connectivity is required for this. | ||
Revision as of 13:41, 31 December 2016
Subject based free and open educational applications
The Free and Open Source Software community has developed hundreds of educational applications, which teachers can use to teach their subjects. These tools complement and supplement the traditional teaching methods that teachers use, such as lecture, chalk and talk, group discussions, projects etc. These tools have a few potential advantages:
- Many of them are interactive and allow for the learner to provide inputs and get feedback/responses and create resources / digital artefacts. This can support a constructivist approach. One of Piaget's contemporaries, Seymour Papert conceptualised this process as 'Constructionism'
- Resources created by the learner can be assessed by the teacher for conceptual understanding
- Peer learning possibilities amongst learners can be supported by encouraging group learning (this can take advantage of the limited ICT resources that may be available in the school, due to which a 2:1 or even 3:1 learner:computer ratio may be required)
- Sometimes intangible or abstract concepts (such as an atomic model, algebraic equations) can be demonstrated through simulations, which can aid conceptual understanding
Free and Open Source educational applications bundled with GNU/Linux operating system
The Free and Open Source (FOSS) GNU/Linux operating system can be configured to add other FOSS applications also, this is not possible to do with proprietary operating system software. The Ubuntu GNU/Linux operating system has been customised to create distributions containing thousands of free and open source software packages, with educational tools for almost all subjects, including Mathematics, Science, Social Science, Language, Art, Music etc. See image below for the applications available in the Education menu sub bar.
More educational applications can be downloaded from the Ubuntu Software Centre, internet connectivity is required for this.