Learn Ubuntu
Introduction
ICT Competency
Operating systems use a program called the Graphical User Interface (GUI, which is pronounced as goo-ee). It allows you to access other computer programmes (applications) by using a mouse. The popular operating systems are Microsoft Windows, GNU/Linux and Mac OSx. In this section, you will learn about the functions of an operating system, using an example of Ubuntu GNU/Linux operating system. With this learning, you can operate a computer with Windows of Mac operating systems
Educational application and relevance
Ubuntu is a ‘Free and Open Source Software’ (called FOSS in short). While software applications like Microsoft Windows or Adobe Photoshop are ‘proprietary’ , meaning they cannot be copied or shared or modified by us, FOSS applications are licensed under the ‘General Public License’ which allows all of us to share the software freely, we can also modify the software as per our needs.
Hence it is important to use FOSS in our schools. Teachers must learn and teach FOSS and avoid use of proprietary software, since it is not possible for all to access and use proprietary software.
Since all the software like Office, web browser, educational software can be bundled with Ubuntu GNU/Linux operating system, so all applications can be installed on the computer at one time. On proprietary software Windows, each software has to be separately installed, which makes it cumbersome and complicated.
There are a large number of freely shareable educational tools on GNU/Linux, pertaining to mathematics, science, social sciences etc which can be used in all schools.
There are large number of additional tools on GNU/Linux freely shareable, such as IBUS which supports word processing in more than 50 languages, including all languages used in Karnataka such as Telugu, Assamese, Tamil, Urdu, Marathi, Hindi etc. or the ORCA screen reader necessary for the visually handicapped or Scribus for desktop publishing.
Version
In once in a six months, Ubuntu is releasing new version of the ubuntu. The first Ubuntu release coincided with the release of Ubuntu 4.10 which was codenamed "Warty Warthog". The recently released version of Ubuntu is 16.10 (as December 2016), but Ubuntu 16.04 is the latest LTS(Long Term Support) version.
Configuration
Processor: 2 GHz dual core processor or better
Memory: 1GB of RAM (2GB recommended)
Disk: 30GB of disk space depending on options
Graphics: If you plan to use the netbook interface, you will require a graphics card that supports 3D acceleration on Ubuntu. Most netbooks are supported very well and shouldn't be problematic.
Either a DVD drive or a USB port for the installer media.
If your computer is not matching any of the above hardware specifications, and you are is old computer, install Lubuntu OS. Lubuntu is Ubuntu based distribution and it is meant for low hardware configuration computers.Lubuntu is a fast and lightweight operating system. It has very low hardware requirements Download Lubuntu ISO 32bit from here and 64bit here.
Overview of Features
Ubuntu is the Linux Terminal Server Project and many applications relevant to education including GCompris, KDE Edutainment Suite, Sabayon Profile Manager, Pessulus Lockdown Editor, Ubuntu Menueditor, LibreOffice, Gnome Nanny and iTalc. Ubuntu CDs were previously available free of charge through their Shipit service; since version 8.10 (2008) it is only available as a download in a DVD format.
Edubuntu's default GUI is Unity while GNOME is still available.[1] Unity has been the default GUI since the release of 12.04. Since release 7.10, KDE is also available as Ubuntu KDE. In 2010 Ubuntu and the Qimo 4 Kids project were working on providing Qimo within Ubuntu,[2] but this was not done as it would not have fitted on a CD.
System software and application software
Operating system is also called system software as it works with the hardware. Every computer must have an operating system to run other computer programmes. Even your mobile phones will have an operating system. Operating systems start automatically when you turn on the computer, this process is termed booting. All the other computer programmes like programmes to paint, type, listen to music, learn maths etc., are called application software or 'Apps' which work with the system software.
Other similar applications
In reality, hundreds of Linux distros are in daily use; DistroWatch.com features a top 100 list of the current most-downloaded distros, where Mint, Debian, Ubuntu, openSUSE, and Fedora hold the top 5 spots. Now, if you're new to Linux, Ubuntu is a very good place to start off.
Development and community help
There are many community forums are helping Ubuntu users.
Working with the application
Functionalities
|
| |
| Step 1-Logging in :
When you switch on your computer, you will see a login screen, login with the user id(name) and password created by the system administrator. Ubuntu allows you to have a user interface in your own language, by specifying your language as the user language, during your user id creation. The applications menu at the top left has a list of all the programmes (apps) on your computer. The Places menu, next to it, lets you access the hard disk, CD/DVD or pen drives. Digital cameras and MP3 players are also listed here when plugged-in. The Applications menu has sub menus for Education, Office, Internet, Games etc. Each sub-menu has many applications. You can try to learn them yourselves by clicking and selecting options. “Self learning” is an important possibility with ICT. Try, Learn, Enjoy. |
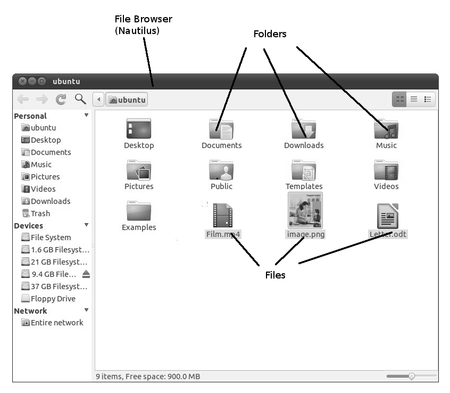
Step 2- Creating and managing files and folders
When you write an essay or paint something on a paper, you would like to keep it for future, right? You would probably put it in a hard bound folder. Maybe, if you have more than one essay or painting, you would have one folder to hold your essays and one folder to hold your paintings. | |
|
| |
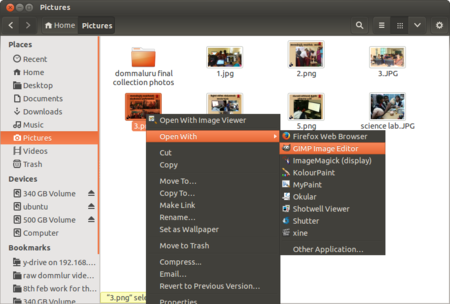
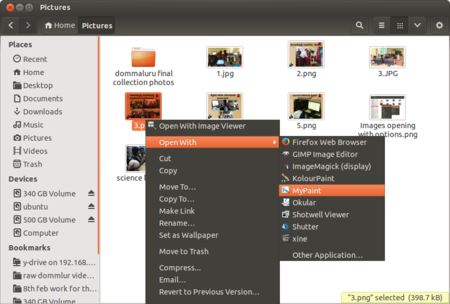
| Step 3-Any file can be opened with any given application in Ubuntu which support that particular file. For example, an image file can be opened with image viewer, gimp, etc.,. So if you want to open the with a application of your choice, right click on file select "Open with" to see the available options. | Step 4-File can be opened with multiple application in Ubuntu which support that particular file. For example, an image file can be opened with image viewer and also can be with Gimp, Mypaint, Kolorpaint, Shotwell viewer etc. So if you want to open the with a application of your choice, right click on file select "Open with" to see the available multiple options. | |
|
| |
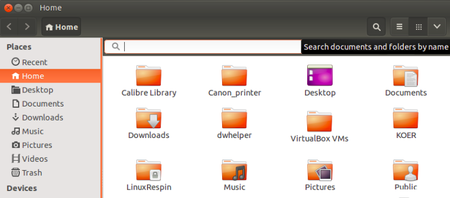
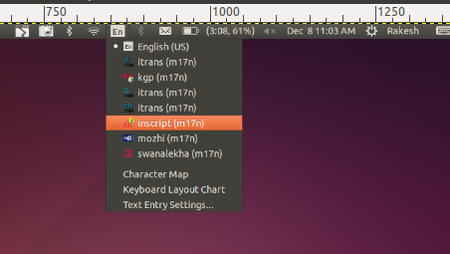
| Step 5 -From HOME folder we can search any files and folders which we have saved in our computer, click on search option at tooldbar and type the keywords of the file or folder, it will show the all files contains our searching keywords. | Step 6 -In Ubuntu OS, you can make typing in our local languages. For example: If you want to make text document in Kannada, just go to top panel and click on "En", here you will get different language options and you can select Kannada(kgp or itrans) language and start typing. If you want add more local languages here, click on "Text Entry Settings" and add languages which you would like to add. | |
|
| |
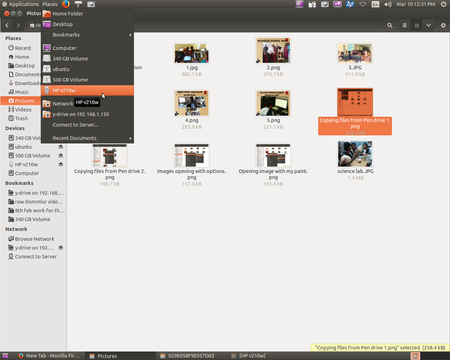
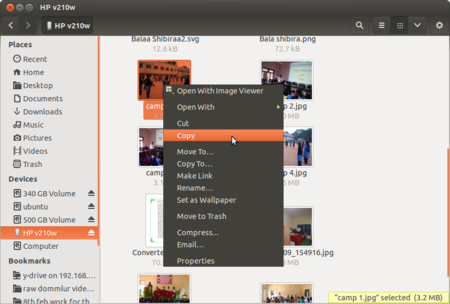
| Step 7- You can Import images from other devices, either by inserting the device into your computer - CDs, DVDs, memory cards can be inserted. Or by connecting the device to your computer, pen drives, memory card holders, external DVD drives can be connected. You should click on "Places" from your desktop top panel. You can see your device name. Click on that to explore files in that device. Study how there are different kinds of connecting cables, for different devices / ports on your computer. Use the appropriate cable in each case. | Step 8- To import files from devices, right click on that file and click on "Copy", then paste it into your computer folder.
You can copy audio and video files, that you have recorded on your mobile phone, to your computer. You can edit these files. In the same way, you can copy these and other files from your computer to your mobile phone. | |
|
| |
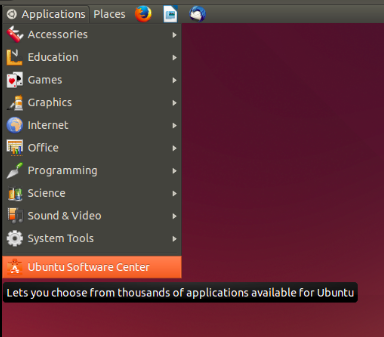
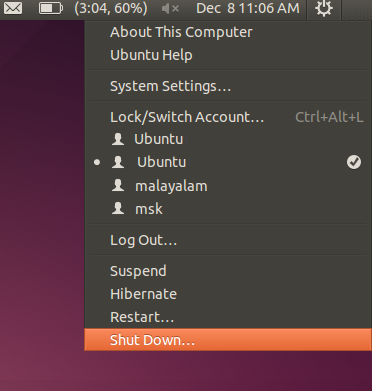
| Step 9- Ubuntu software centre - to download applications from the Internet. teachers can explore new foss educational tools and utilities | Step 10-Logging in :Shutting down the computer
What will you do after you have finished your work? You have to turn off the computer. You must turn it off by clicking on the last button on the right hand top corner and select shut down. Never turn off the power button without shutting the computer properly. If you have doubts or difficulties in using the Ubuntu operating system or any of the applications, you can search for solutions on the Internet using a search engine. You can also find 'frequently asked questions and answers' on http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Frequently_Asked_Questions.. |
File formats for creation
Not Applicable
Saving the file
Not Applicable
Export and publishing files
Not Applicable
Advanced features
Ubuntu contains a wide range of software that includes LibreOffice, Firefox, Thunderbird and several games and Educational tools. Many additional software packages are accessible from the built in Ubuntu Software Center as well as any other APT-based package management tool.
Installation
To install UBUNTU into different version OS, please refer Kalpavriksha page for detail steps.
| Telugu
|
Kannada
|
|---|
Primary Steps to install UBUNTU
1.Using a DVD?-
It’s easy to install Ubuntu from a DVD. Here’s what you need to do:
Put the Ubuntu DVD into the DVD-drive
Restart your computer. You should see a welcome screen prompting you to choose your language and giving you the option to install Ubuntu or try it from the DVD.
2.Using a USB drive?
Most newer computers can boot from USB. You should see a welcome screen prompting you to choose your language and giving you the option to install Ubuntu or try it from the USB.
If your computer doesn’t automatically do so, you might need to press the F12 key to bring up the boot menu, but be careful not to hold it down - that can cause an error message.
3.Prepare to install Ubuntu- We recommend you plug your computer into a power source
4.You should also make sure you have enough space on your computer to install Ubuntu.
We advise you to select Download updates while installing and Install this third-party software now
You should also stay connected to the internet so you can get the latest updates while you install Ubuntu
If you are not connected to the internet, you will be asked to select a wireless network, if available. We advise you to connect during the installation so we can ensure your machine is up to date
5.Allocate drive space-
Use the check boxes to choose whether you’d like to Install Ubuntu alongside another operating system, delete your existing operating system and replace it with Ubuntu, or — if you’re an advanced user — choose the ’Something else’ option
6.Begin the installation
Depending on your previous selections, you can now verify that you have chosen the way in which you would like to install Ubuntu. The installation process will begin when you click the Install Now button.
Ubuntu needs about 4.5 GB to install, so add a few extra GB to allow for your files.
7.Select your location-
If you are connected to the internet, this should be done automatically. Check your location is correct and click ’Forward’ to proceed. If you’re unsure of your time zone, type the name of the town you’re in or click on the map and we’ll help you find it.
Select your preferred keyboard layout
Click on the language option you need. If you’re not sure, click the ’Detect Keyboard Layout’ button for help.
8.Enter your login and password details
After this, Install process will get start and it may take 20-40 min to complete. once its done it will ask you to remove the device and restart that system.
The application on mobiles and tablets
Ubuntu is available on select Mobile phones and tablets
