Learn wisemapping
Introduction
Basic information
| ICT Competency | WiseMapping is a free, web-based mind mapping tool that allows users to create, share, and collaborate on mind maps online. This guide will help you understand how to use WiseMapping effectively for your projects'. |
| Educational application and relevance | Making concept maps can support thinking, brainstorming, sharing information and documenting meetings and group processes.
Educators consider that concept mapping is a good approach for building skills in students for ideating and organizing ideas; they also find it a great asset for teaching. It is a great tool for students to help them organize their thought processes when writing. Teachers and students can use this application to collaboratively or individually create concept maps on an idea or explore a problem. |
| Version | Version - 6.0 |
| Configuration | This tool has no specific configuration requirements. It is a web-based application accessible through any modern web browser. WiseMapping is available for use on all major operating systems, including Windows, Mac, Linux, and Android (not stable). |
| Other similar applications | teammapper |
| The application on mobiles and tablets | MiMind & teammapper |
| Development and community help | wisemapping |
Overview of Features
WiseMapping helps you create and manage mind maps with ease. It allows for the organization of ideas into a structured format that can be visually represented. The tool is entirely web-based, facilitating easy access and collaboration from any location without the need for installation. It offers features like:
- Mind Map Creation
- Linking Resources
- Annotations and Notes
- Rich Icons
- Hierarchical Organization
- Collaboration
- Embedding and Exporting
- Customizability
Setting Up a WiseMapping Account
Creating an Account
- Visit the WiseMapping Website
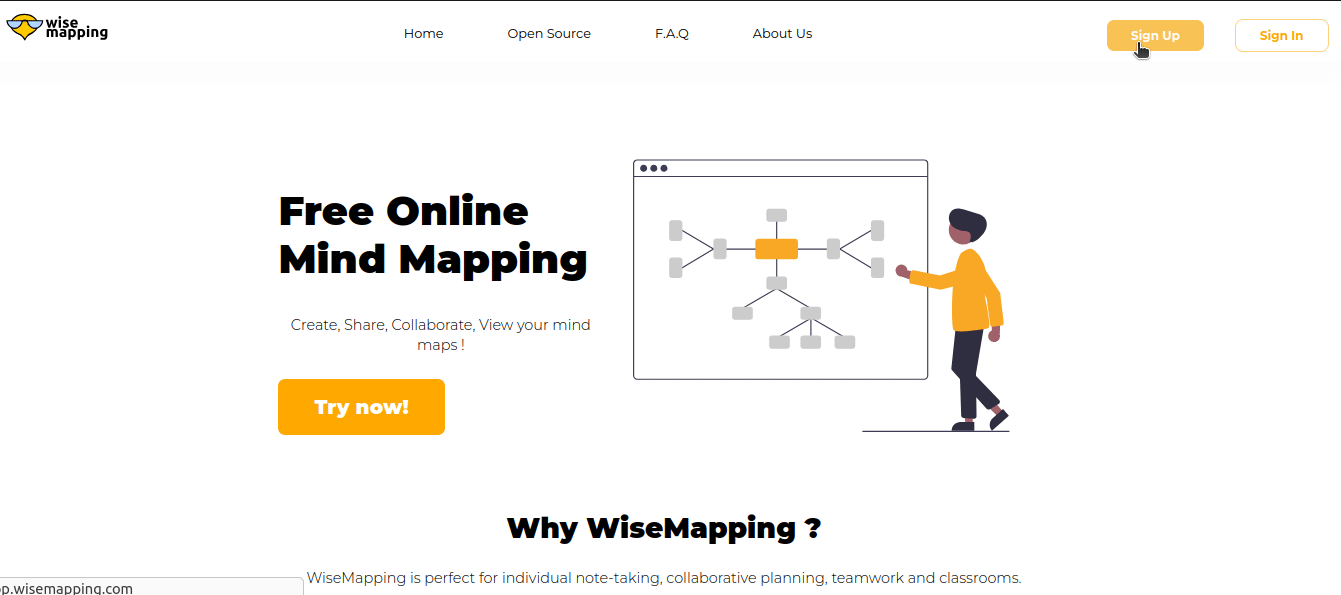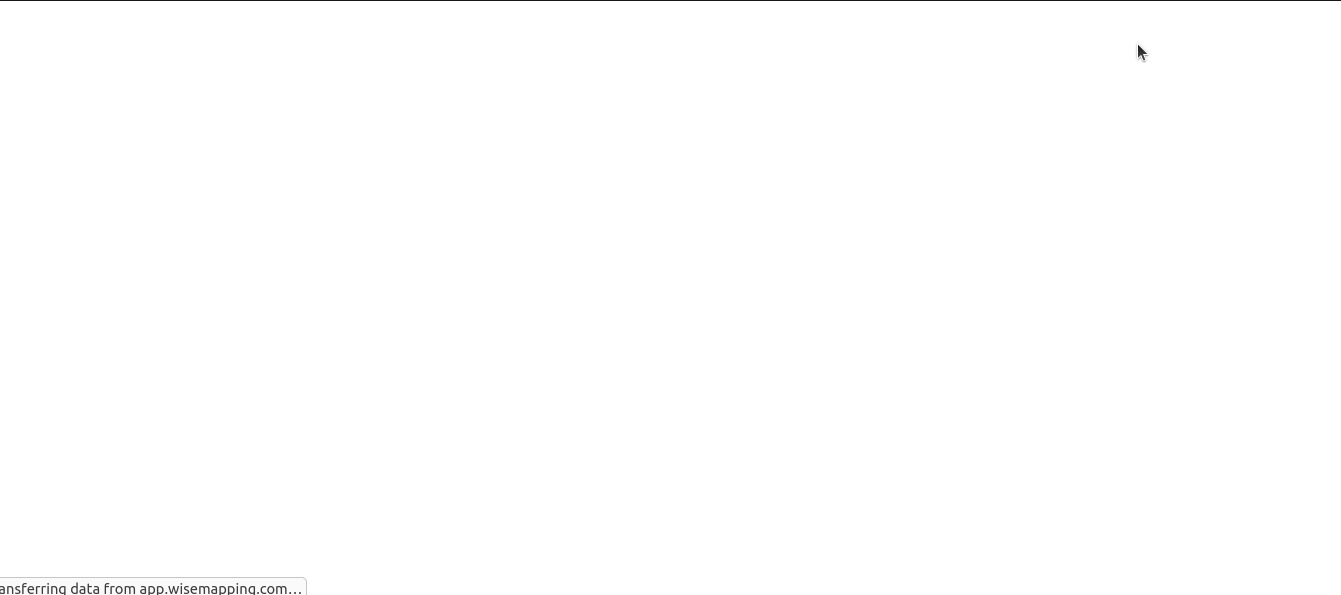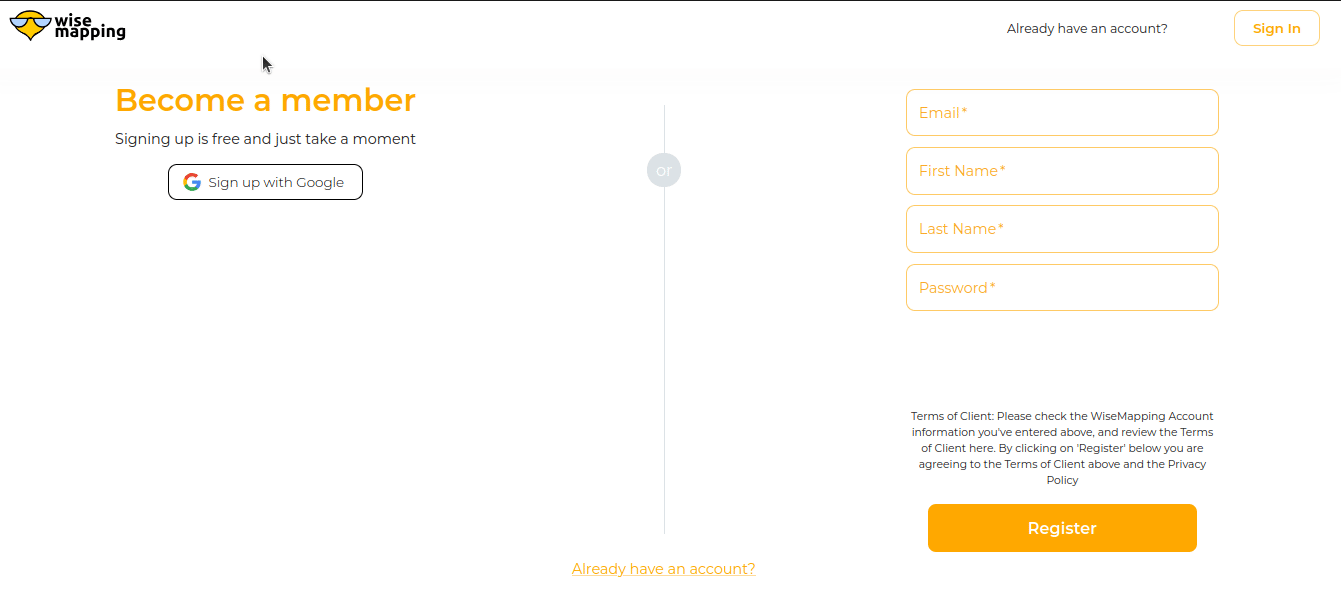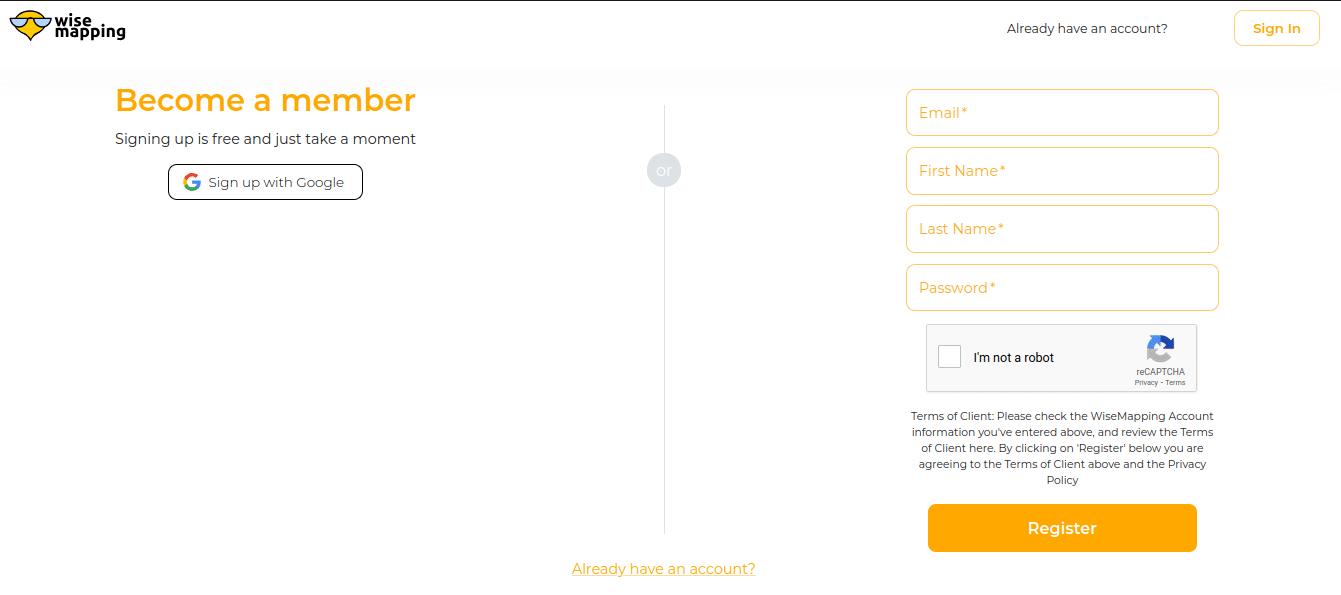
Sign Up
Click on the "Sign Up" button at the top right corner
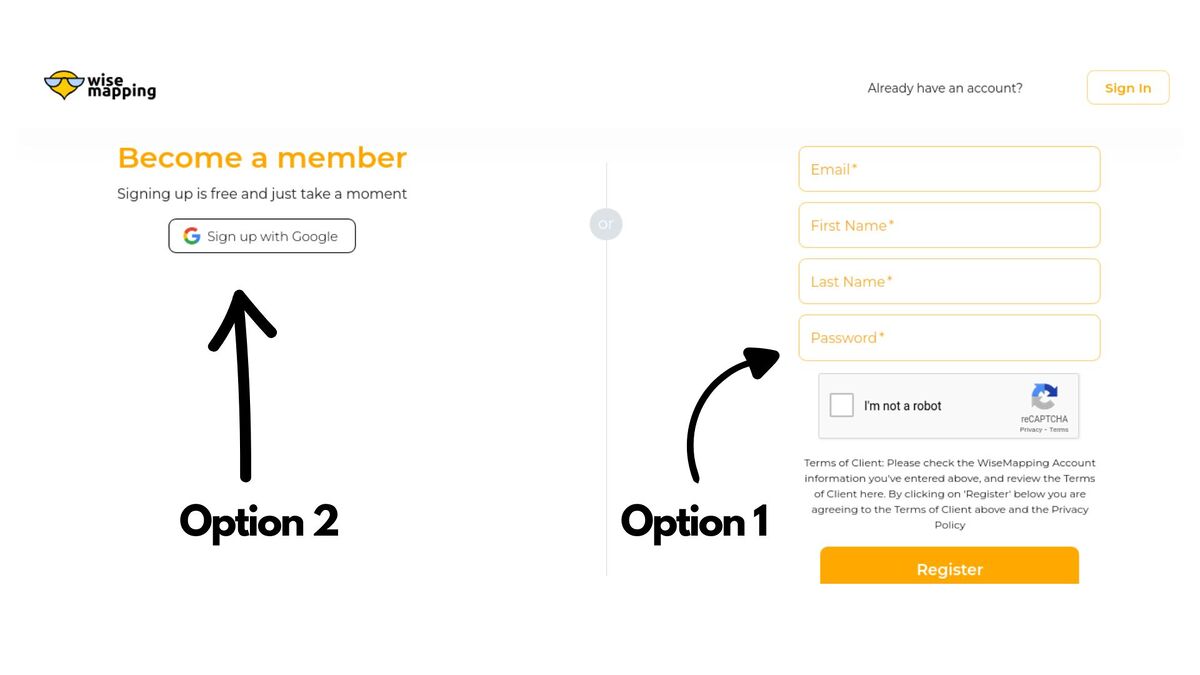
Choose a Sign-Up Method:
You will be provided with two options:
- Option 1: Fill in the required information (username, email, password) and complete the captcha.
- Option 2: Sign up with a Google account. This option will ask for permission to choose your email. Select your email ID and click Continue.
Complete the Process:
Once you click "Continue," your account will be created within a few seconds
![]() Note: Option 2, signing up with a Google account, is much easier than Option 1, the traditional sign-up method.
Note: Option 2, signing up with a Google account, is much easier than Option 1, the traditional sign-up method.
Working with the application
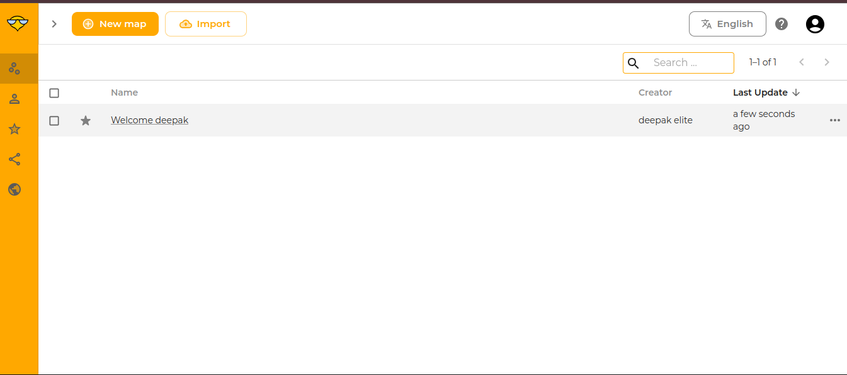
To learn working with WiseMapping, we will start by creating a concept map. Upon signing up or logging in to WiseMapping, you will see an interface similar to the one shown above. WiseMapping provides a demo mind map named "Welcome, [Your First Name]!" based on your Gmail account. This mind map is given by WiseMapping to help you understand its functionalities and features.
Creating a map
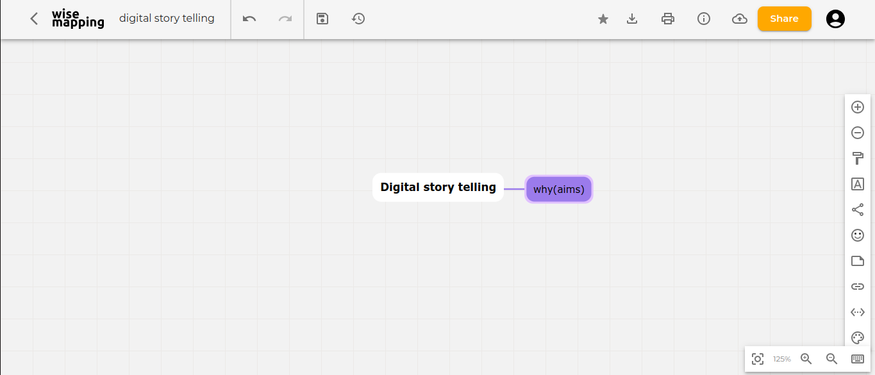
To create a mind map, go to the top left corner of the interface window and click on "New map." Once you click on "New map," it will ask for the map name. I will input "Digital Story Telling" as my map name. You will also need to fill in the description of the map to help others understand what your mind map is about when you share it. Once you click "Create," it will create the mind map.
- Error creating thumbnail: convert: memory allocation failed `/home/tnet/public_html/OER/tmp/transform_f574053011b3.gif' @ error/quantize.c/QuantizeImage/2653.
convert: memory allocation failed `/home/tnet/public_html/OER/tmp/transform_f574053011b3.gif' @ error/gif.c/WriteGIFImage/1693.
Error code: 1Creating a mindmap
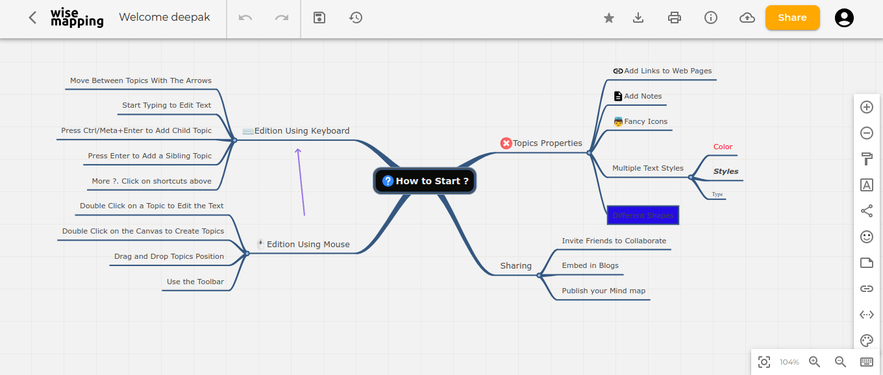
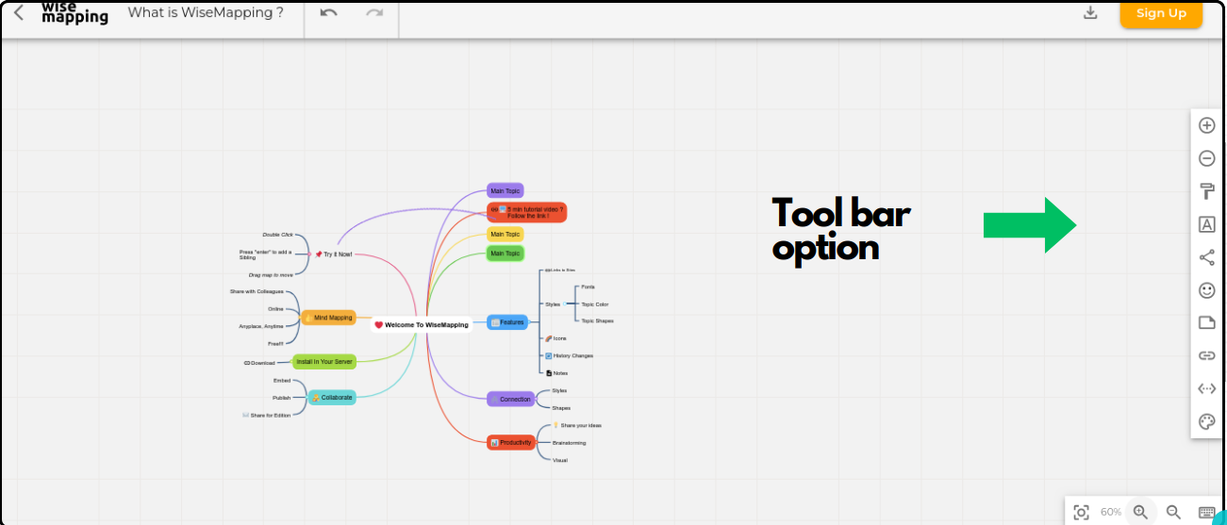
Toolbar Features
Once you create a map in WiseMapping, you'll see toolbar options on the right side. This toolbar helps you create a feature-rich mind map
The features includes:
- Add Topic: Insert new topics into your map.
- Delete Topic: Remove unwanted topics.
- Topic Style: Customize the appearance of topics.
- Font Style: Change the font of your text.
- Connection Style: Adjust the style of connections between topics.
- Icons: Add icons to topics.
- Notes: Attach notes to topics for additional information.
- Links: Insert hyperlinks into your map.
- Add Relationship: Create relationships between different topics.
Theme: Apply themes to your mind map for a cohesive look.
Inserting nodes
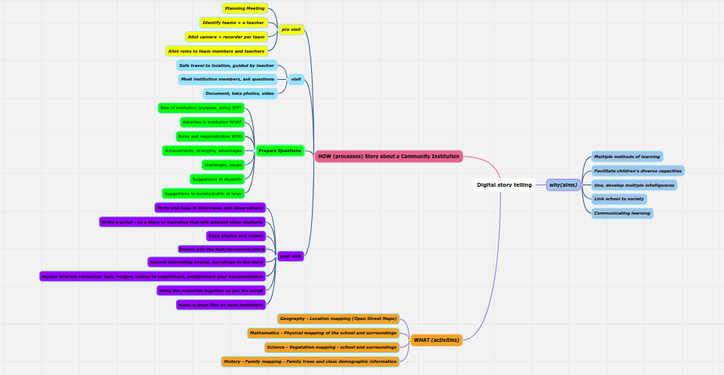
Here as an example, we have created a concept map called Learning Digital Story Telling. After the root node is created, additional ideas are added by adding more nodes, called child nodes. The concept map gets built by adding further child nodes, for topics and sub-topics. You can keep adding child nodes to any node.
- Use the ‘insert’ key to create a ‘child node’ this is a sub-concept of your current concept.
- Use the ‘enter’ key to create a ‘sibling’ this is a parallel concept to your current concept.
Thus you can create a concept map with knowing just two functions – add child node (insert) and add sibling node (enter). In this manner, a concept map can be used to classify and categorize information.
- Child and sibling nodes
Our map has nodes for the ‘why’, ‘what’ and ‘how’ of DST, with sub-nodes.
- The first image shows the creation of a concept map with the first child node.
- The second image shows the completed concept map with child nodes and sibling nodes.
![]() Note: You can zoom in and zoom out the map as needed. To do this, click the zoom in and zoom out icons located in the bottom right corner of the interface.
Note: You can zoom in and zoom out the map as needed. To do this, click the zoom in and zoom out icons located in the bottom right corner of the interface.