Difference between revisions of "TE year1sourcebook/Topics of Study in the Unit"
| Line 378: | Line 378: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | ==== | + | ====Student activity time (3 hours) ==== |
#You will need to create an email id for yourself, this is like a digital post-box or digital address. You can create an email id using a Gmail on <nowiki>http://gmail.com</nowiki>. Login by providing your 'user id' and then 'your password'. Compose an email and send to another student whose id you know. Compose an email discussing some of the resources you saw on your topic and ask for your classmate to give suggestions and feedback on your resource. Copy your teacher's email id in the 'cc'. | #You will need to create an email id for yourself, this is like a digital post-box or digital address. You can create an email id using a Gmail on <nowiki>http://gmail.com</nowiki>. Login by providing your 'user id' and then 'your password'. Compose an email and send to another student whose id you know. Compose an email discussing some of the resources you saw on your topic and ask for your classmate to give suggestions and feedback on your resource. Copy your teacher's email id in the 'cc'. | ||
#Receive emails in your 'inbox' from your classmates. Open and read them. 'Reply-to' the sender of the mail and give your comments on the mails from your classmates. | #Receive emails in your 'inbox' from your classmates. Open and read them. 'Reply-to' the sender of the mail and give your comments on the mails from your classmates. | ||
| Line 385: | Line 385: | ||
References: [[Learn Gmail]] | References: [[Learn Gmail]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
=== Equitable access to ICTs === | === Equitable access to ICTs === | ||
Revision as of 04:27, 10 May 2017
The topics of study in Unit 1 are
A brief history of ICT
The term 'ICT' refers to those set of technologies that help us create information, access information, analyse information and communicate with one another. Most of you must be using a cell phone to communicate, which even fifteen years ago would not have been the case with most students. A cell phone is a digital information and communication device, a part of the recent ICT revolution. Yet ICT are perhaps nearly as old as humanity itself, as human beings needed to communicate with one another, beginning with symbolic (non verbal) ways, before language was invented. Language can be seen as the first 'ICT', it enabled (oral) communication amongst human beings.
Script was the next ICT, invented around 5,000 years ago, which enabled information to be held distinct from the communicator and be made available beyond the limitation of space and time that oral communication imposed. You would be learning more about the processes of speaking and listening (comprising oral communication) and reading and writing (comprising written communication) in your courses on language learning. Writing also enabled easier recording of human history and thus the invention of script was a landmark in the history of ICT. Invention of printing technologies scaled up the 'writing' process and enabled mass production of books. The invention of radio and television created the 'mass media' in which simultaneously the same message could be transmitted to thousands of people. Each ICT invention enabled the processes of information creation, sharing, storing and communicating to be easier, quicker, more efficient, enabling greater reach. Each ICT invention was a significant event in the evolution of human communication processes and caused an explosion in the availability of information. While human beings have always accessed information and communicated, what makes the present ICT special, is their digital nature, hence we can even refer to ICT as 'digital technologies'.
A brief history of ICT is provided in the table below
| Knowledge model / Basis | Method | Storage | Sharing | Publishing (mass sharing) | Features |
| Oral / Language | Oral | Human memory | Speaking - Hearing | Not possible | Requires synchronicity of space and time. |
| Written / Script | Text | Books | Physical | Not possible | Share knowledge across space and time, but in a limited manner |
| Print / Printing | Text | Books | Physical | Books | Explosion of information, due to large volume of books being available; information could be made available on a much larger scale |
| Mass Media/ Radio, TV | Analog/ Digital - Audio, video | Cassettes and similar analog devices | Physical | Broadcast transmission equipment | Mass reach across wide geographies |
| Digital (ICT) | Digital methods (text / audio / video editors) | Digital storage like hard disks | Websites, blogs, Wikis – 'desktop publishing' | Information spreads fast and wide. Much easier construction and much wider possibilities – text, audio, video. Formats of information can be combinedd |
Digital ICT
We are now perhaps in the middle of the next epochal movement in the history of ICT - the use of digital methods of accessing, creating, modifying sharing, storing information as well as for communication. Most of you would have been born after the beginning of the mass use of cell phones (the second generation or 2G cell phone technology was available for mass use from 1991), towards the end of the first millennium, while many teacher educators would have been born before this period! This phenomenon creates an interesting inversion in the school environment, in almost all other areas, the teacher (teacher educator) is more familiar than the learner (student teacher), while in case of ICT (more specifically in the skill of using ICT devices and methods), it can often be the opposite! Younger people may often pick up a technology quicker than older people. However, digital literacy does not only mean skills but rather On the other hand, the experience and insights of teacher educators can help student teachers develop a critical perspective towards digital ICTs, which is essential, since digital ICTs have huge potential for doing harm as well as good.
You will learn to use digital ICT for two purposes in the first year - 'connecting and learning' and 'creating (generic resources) and learning', in the two units respectively. Before 'connecting and learning' you need to have a basic familiarity with the ICT devices and tools.
Basic familiarity with ICT devices and applications
What all can a computer do?
Have you ever wondered why a computer is different from a fridge? One clue to the difference is the number of things a computer can do. You can read a book, type a book, listen to music, play a video or access the internet. Now your smart phone can also do many of these things. What makes all these things possible is the operating system, a software that allows the computer to process inputs through the keyboard or mouse, process it and produce an output. An operating system software allows different parts of a computer to work together; an application software allows for different kinds of processes to be accomplished by the computer.
A computer is a device which takes input, processes it and gives output which can be stored and shared. When you enter data into your computer, it is called as input. An input can be data like text or picture or an instruction on what to do with the data. This data is processed (process means to perform a series of operations on a set of data) and you will get the output. The software is what makes the computer and mobile so powerful. Learn more about the history of computers. Like computers, tablets and mobile phones also allow you to process and share information digitally.
The ICT environment
Any technology has a skill component and ICT is something all of us can practise for our own use. In the next section we will learn how to use a computer and various software applications for our professional activities. We will explore the basics of computer hardware and software and learn Internet browsing, concept mapping as well as text and number editing applications in this section. At all times, we will try to see how ICT are relevant to your primary mandate of teaching-learning. Hence we will approach the learning and use of these applications from a pedagogical perspective.
ICT environment - Hardware
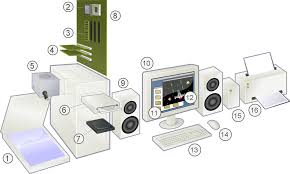
ICT refer to an entire range of devices that use digital methods to process represent and communicate information. The desktop computer, laptop, tablet and the smart phone are all ICT devices. Let us explore below the parts of a desktop compute
| 1. Scanner (nowadays scanning function is available in the mobile phone, hence a separate scanner is not often used) | 2. CPU (Central Processing Unit): does the processing work of the computer. It contains “chips” which determine the speed of computer. For example i5 is a chip manufactured by Intel. |
| 3. RAM (Random Access Memory): This is the storage space in the computer. Temporally it will store frequently used applications and data in it, to increase the speed of the computer. The size of RAM determines how fast the computer works | 4. Expansion cards. |
| 5. Power supply unit, which supplies power to the computer. | 6. CD Drive – External storage device. This is now becoming obsolete as USB storage devices / 'pen drives' are becoming more popular |
| 7. Hard disk: Hard disk stores the user data as well as the software. This storage capacity of the computer is specified in terms of GB (Gigabytes), 1 GB = 109 bytes or 1000,000,000 bytes | 8. Motherboard: This is where all instructions are wired together and helps the computer work |
| 9. Speakers, these amplify any audio played on the computer | 10. Monitor, for displaying our instructions to the computer and its responses. Monitor consumes quite a bit of electricity, so should be kept in the 'off' mode when the computer is not being actively used |
| 11. Operating System. An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs. All computer programs (application software) require an operating system to function. | 12. Application Software - An application program (app or application for short) is a computer program designed to perform a group of activities. Examples of an application include a text editor, a spreadsheet, a web browser, or a photo editor. The collective noun application software refers to all applications collectively |
| 13. Keyboard, similar to a type writer keyboard. It is an input device, used for typing instructions (text, numbers, special characters) to the computer. | 14. Mouse, another input device, that works on the Graphical User Interface of the computer |
| 15. External Hard Disk, additional storage space. | 16. Printer, output device |
Hardware: Parts 2-8, 10, 13 and 14 constitute basic hardware and are parts of all computing devices. These have now all been combined into one unit in a laptop or mobile. Largely, the hardware is divided into input devices and output devices and storage functions.
| Input Devices | Output Devices |
|---|---|
| Mouse | Monitor |
| Keyboard | Projector |
| Microphone | Printer |
| Scanner | Speakers |
| Web cam |
ICT environment - Software
We saw earlier that each ICT device must have an operating system (also called system software) to run other applications or programmes. Operating system starts automatically when you turn on the computer, this process is termed booting. All the other software to paint, type, listen to music, learn maths etc., are called application software or 'Apps' which work with the system software. We will use the Ubuntu ‘Free and Open Source Software’ (called FOSS in short) operating system for our paper. Operating systems use a program called the Graphical User Interface (GUI, which is pronounced as goo-ee), to access the computer with a mouse. The popular operating systems are Microsoft Windows, GNU/Linux and Mac OSx. You will learn about the functions of an operating system, using an example of Ubuntu GNU/Linux operating system. With this learning, you can also operate a computer with Windows of Mac operating systems. Since Ubuntu is a FOSS operating system, FOSS applications like Office suite, web browser, educational software can be bundled with Ubuntu GNU/Linux operating system. All these applications will be installed on the computer along with the operating system.
Installing operating system on the computer
Ubuntu installation is quite simple, and can be done by an average computer user. The minimum hardware required to install Ubuntu in a computer is:
- Minimum 40GB or above free space / separate partition in hard disk.
- Minimum 2GB RAM (4GB and above preferred)
- DVD reader or USB port
Electric power should be available during the installation process. You will need the Ubuntu software in a DVD or in a pen drive (as a boot-able USB device). If you are installing an operating system on a computer that is being used, please be sure to take a back up of the data on an external storage device.
In the computers in your lab, a custom distribution of Ubuntu GNU/Linux operating system which contains all the educational software applications and utilities required to transact this paper, would have been installed. A copy of the Ubuntu custom distribution could be obtained from DSERT, if required. In case you need to install the system on the institution computers, or you would like to install in your own computer, you can do so. Being able to install the operating system itself on your computer is an empowering process. In many cases, if you face problems while using your computer, including serious issues such as hard disk crash, you can re-install the operating system to start using your computer again. The installation process for the custom Ubuntu GNU/Linux system is available in this document and you can become more familiar with your computer by exploring it.
Interacting with the operating system
Ubuntu performs other basic functions expected of an operating system, including the following:
- You can login and logout, and your user data will be secure within your own login
- Logging in: When you switch on your computer, you will see a login screen. Login with the user id (name) and password created by the system administrator. Ubuntu allows you to have a user interface in your own language, by specifying your language as the user language, during your user id creation. Once you have logged in, the home screen will appear.
- Shutting down the computer- After you have finished your work, you have to turn off the computer. You must turn it off by clicking on the last button on the right hand top corner and select shut down. Never turn off the power button without shutting the computer properly, as it can cause files to corrupt.
- Users can browse (and search for) the folders and files on the computer using Nautilus file browser
- Users can use different applications on their computer for creating and accessing files. You will learn some of these applications in unit 2 (generic resource creation). The custom Ubuntu distribution comes bundled with a large number of educational applications as well as generic text, image, audio, video, animation resource authoring tools.
- Users can connect to other ICT devices - printers and scanners, mobile phones, pen drives, external hard disks and storage devices, external DVD writers etc.
- Users can connect to their local area network and the internet.
Adding FOSS applications to your computer
While Ubuntu will come bundled with many applications, you can also add more FOSS applications to your computer. Go to Applications > System Tools -> Software. You will need to type the required application name in the search bar. It will show all
applications with the words you have entered and you will get an option for "Install". Click on "Install" if you want to install the application. If your search does not get the application(s) you want, try with fewer letters / words to search . It may ask your Ubuntu log in password for authentication, just type your Ubuntu password press enter.
As explained in the overview, practice activities will be provided at relevant points in the source book, to integrate theory and practice. These practice activities will need to be done in your ICT Lab.
Learning to input with keyboard
Most of the instructions / input is given to the computer through the keyboard, hence it is important that teachers should be able to type efficiently, using all their fingers. Typing using the correct finger for each key on the keyboard will help improve the speed of input enormously. It will enable the teacher to type without seeing the keyboard, and seeing the monitor during typing, will enable spotting of any mistakes immediately. Earlier to learn typing, one had to go to a typing class, but now the computer has Tux Typing software that you can use to learn typing.
The keys on the keyboard can be divided into several groups based on function:
- Typing (alphabets and numbers) keys: These keys are arranged as in a traditional 'QWERTY' typewriter
- Special purpose keys: These keys are used alone or in combination with other keys to perform certain actions, such as CTRL, ALT, ESC, Function keys etc.
- Navigation keys: These keys are used for moving around in documents / editing text. They include the arrow keys, HOME, END, PAGE UP, PAGE DOWN, DELETE and INSERT.
- Numeric keypad: The numeric keypad is handy for entering numbers quickly. The keys are grouped together in a block like a conventional calculator or adding machine. This block may not be available on all keyboards, numbers are also provided in the top rung of the keyboard
Working with the Tux Typing application
To open Tux Typing go to Application > Education>Tux Typing
- Starting typing practice
- Starting typing practice
- Tux Typing home screen / main page
- Tux Typing lessons
- Keyboard layout
- When you open the Tux Typing it will show the window as shown in the first image. Typing can be practised by selecting games and lessons.
- When you select the lesson option it will show the window as in the second image. There are 43 basic lessons. Go through the each lessons to practice typing.
- When you select a lesson, Tux Typing will show a window and ask you to press space bar and then the "p" key. If the 'Caps Lock' key is on (to type CAPITAL Letters) then Tux Typing won't work. Hence make sure this key is not on.
- After you practise these lessons, you will find that you can use all your fingers for typing. This speeds up your typing hugely. You need not look at the keyboard to type, so you can see the monitor as you type, which enables you to identify mistakes in typing.
Start practice typing
After clicking 'space bar' and 'p' key it will show the window as above. On the screen you can see items - Time, Chars (characters), CPM, WPM, Errors and Accuracy; these basically tell you how well you are typing. You will find a blinking button on each finger to guide you as to which finger to be used for typing a given character. There will also be a blinking light around the character to be typed.
Learning to input with the mouse
Initially, the keyboard was the only device for providing instructions to the computer, but with the invention of the 'graphic user interface' (GUI in short), the mouse became an important input device. The mouse makes giving instructions much simpler by pointing the cursor to a place on the screen and clicking to select an instruction. You can become comfortable in using the mouse by practising with Tux Paint. Tux Paint features a simple interface and a fixed drawing area with access to previously made images using icons. Tux Paint is equipped with cartoon mascots which can encourage students to learn to use the mouse.
Student activity time (3 hours)Familiarity with the ICT environment (2 hours) Get familiar with the computer in the ICT lab. You can switch on and switch off the computer and see if you can identify the parts. You can also practice connecting different peripherals. Login to the computer in your ICT lab. Open a few applications and explore what you can do with them. Identify a topic on which you will create a resource, for this course. Typing practice and practice with Tux Paint Creating your cumulative resource folder (1 hour) Over the two units, you will be accessing and creating learning resources connected to this topic, hence identify a topic of interest to you. You should identify a topic (or two), in which you are interested to create resources. Your own work as a student teacher may require you to source / make materials for classroom teaching-learning processes, or you may want to share your ideas and thoughts, as a resource, with your classmates for mutual learning, or you may simply want to create a resource for your self-development. The topic could be from the subject(s) you teach (a science topic like ‘Light’ or a mathematics topic such as ‘number system’ or a geography topic as ‘forests’), or a larger issue in education ('Challenges of teaching in inner-city public schools'), or larger social issue ('global warming'). It will be much more meaningful learning, if as a part of this course, you could access, create and publish a learning resource on a topic which you want to learn/ know more about or need teaching resources. You could create this resource in English or in Kannada or your own language. Create a folder with this topic name, this could be a sub-folder within 'Documents' folder on your computer. Try searching for 'Mathematics' or 'Science' or 'Geography' applications, Ubuntu Software Centre. and install a software you think will be useful for your learning. References: Explore a computer, Learn Ubuntu, Learn Tux Typing , Learn Tux Paint |
ICT for connecting and learning - Accessing the global digital library (GDL)
For making teaching more effective, a resource rich learning environment is necessary. However, in many cases, teachers only have the text book for their subject. The text book is intended primarily for the student and the teacher needs to access resources that are a super set of the topic as dealt in the text book, so that the teacher is well placed to teach the topic using different approaches and wit multiple resources, based on the learning contexts and needs of the students. Teachers must also be resourceful to address any doubts or questions that may arise in class or elsewhere on the topic. However, learning resources other than text books are not easily available to teachers. Also significant part of materials available is copyrighted, meaning teachers cannot make copies of the same for their use and it may be expensive to purchase all the required resource materials.
The internet, a product of digital ICT, has changed the way we think of accessing information or communicating. With the internet, you can connect to any computer in the world and access information and resources. As a 'global digital library, the internet has information on almost every topic. This changes the way we can think of learning and the skills of learning. Skills of accessing information, organizing, evaluating information are very important. While the Internet is a continuous learning resource and there is a lot of content you can access, to make the resources useful, you need to evaluate the resources, organize it well, and have a clear unit plan on how to integrate multiple resources for teaching.
Internet is also allowing new methods of learning through on-line courses and resource repositories. Unit 1 will help you learn how you can use ICT to connect and learn.
What is the internet
The internet is a physical network of millions of computers across the world, each of which has a unique identifier. Some of these computers act as 'servers', they store data which can be accessed by other computers. The Internet is thus like a huge library with information on almost any issue. The 'web-sites' we visit are nothing but folders of computers connected to the internet. Apart from information, many of these computers also have applications or web tools, such as search engine, maps, translation, which have different purposes.
World wide web
World wide web (www) is an application on the internet, which allows computers to access the Internet in the form of a web page, using an application called the web browser. There are millions of pages of shared information on the computers in the network, created by many people and organizations, in the form of 'web pages' accessed using a software application called a 'web browser'.
Information can be accessed in multiple ways from the www and we need to know how to search for it. Sources of information, even if freely available on the Internet, needs to be acknowledged. Resources are available in different formats on the Internet- images, videos, audio files etc. We must be aware of Internet safety while accessing images, videos and other information on the Internet. We already saw that each website is a page on the Internet and has an address. We can either copy and paste the link directly in the address bar of a web browser.
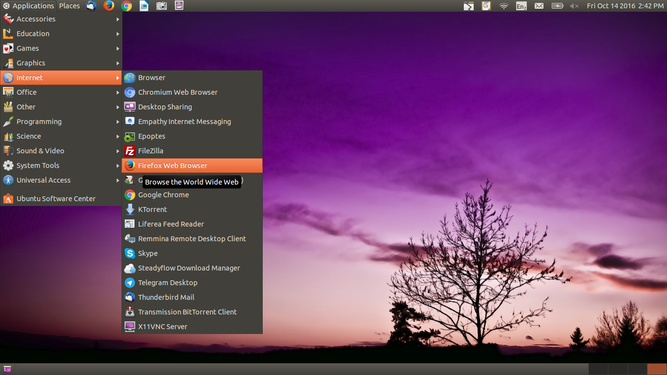
You will access and navigate the internet using a free and open source web browser such as Mozilla Firefox. Mozilla Firefox will appear under Applications > Internet >Firefox Web Browser.
If you know the web address of the site you want to visit, you can type it in the address bar. Ex; http://kn.wikipedia.org. If you don’t know the particular web address, you can type a key word(s) relating to the topic e.g. Wikipedia, using a search engine. Some examples of search engines are Google search engine or DuckDuckGo search engine. You can search not only for text, but also for images and videos You can download the file (video, text file, image file) to your computer.
You will find that much more resources are available for your topic in English compared to Kannada or other languages.
Browsing the internet is taking the tour of the global virtual world, hence it will have rewards as well as expose you to risks and dangers. Refer to the last section in this chapter for Internet safety suggestions.
| An important philosophical justification of using FOSS in education, is that the teaching learning processes should not be constrained by the access to learning resources. While proprietary software is prohibited from being shared or modified, FOSS has been developed to support free sharing and customisation as per needs of the user. Hence in this course, we will only learn to use FOSS tools. However the learning will focus on the processes that the tools support, so that the student-teacher can also easily figure out how to use a proprietary equivalent if required.
While we learn to use the Firefox FOSS browser here, with this learning, a student teacher can easily use a proprietary browser such as Edge from Microsoft. |
Opening and accessing the web browser Firefox
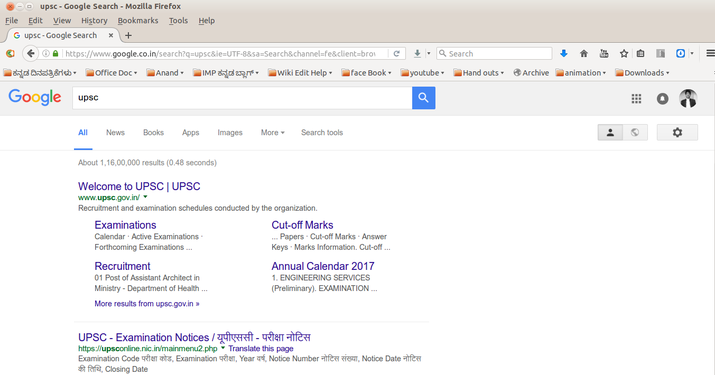
- Mozilla Firefox will appear under Applications > Internet >Firefox Web Browser, as shown in the first image
- If you know the web address you can type it in the address bar. Ex; www.upsc.gov.in. See the second image
- In the third image, you will see how to access a website if you don’t know the particular web address. You can type the key word of searching object Ex;UPSC. You can search not only for text, but also for images, videos using search engine.
- The fourth image shows the Google search engine, the search results has options for searching the web, or images or videos. You can download the file (video, text file, image file) in to computer. Check if the copyright of the file allows to copy and use.
- Using a browser to access the internet
Accessing information on the internet - Search engine
A popular way of finding information on the Internet is through the use of a search engine. Search engine is a website that can retrieve a large amount of relevant information in very a short time.
The search engine has enormous implications for our processes of teaching-learning. In the past, rote learning (remembering information) has been seen as important, since such committing information to memory would allow us to access it when needed. Traditional Indian schools also had memorising scripts as an important learning method. However, with ICT, that has changed. Due to information explosion, it is now impossible to commit to memory the numerous aspects of our daily lives. Secondly, thanks to methods of storage and retrieval, including use of search engines, the need to memorise has also reduced. Twenty years back, we used to remember peoples telephone (land-line) numbers, which were not too many. Now with large number of contacts we have, we do not need to memorise their phone (cell phone) numbers, since we can store it in the phone itself and can retrieve by name. In the same way, any factual information can be retrieved in a fraction of a second and hence not worth memorising.
Thus while in the past, significant amount of teaching was actually the dissemination of information, now that would neither be required, nor would students readily accept it. Teaching has to hence necessarily move to the next order of interpreting, critically reflecting on facts to assess and make meaning. Thus in a way, search engines have done the processes of learning a good turn, by making information transmission as a largely redundant part of learning. On the other hand, they have also enabled easy copying of materials, without requiring much effort to understand, potentially encouraging superficial learning.
Searching text and image resources
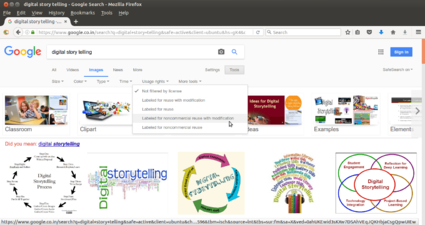
- You could look for text information by simply typing the key word of your searching content, In the first image you can see text information accessed Digital Story Telling" in the search bar of the search engine. You can copy the shown information and can paste into your own text document.
- You can search for images from Firefox web browser, For example: If you want to search images about Digital Story Telling, simply type "Digital Story Telling" in the search bar of the search engine and select ‘Images’ link. Here you can select images that are licensed for reuse by specifying the search settings. If you want to download or save images to your computer, right click on the image and click on "Save image as". In the second image, you will see how to rename the image file and select appropriate folder to save.
- Firefox has in-built search button for Google, DuckDuckGo, Yahoo, Bing and few other popular search engines. The DuckDuckGo search engine does store your searches, which allows you privacy, whereas Google search engine and most other search engines store your searches.
- Searching text and image resources
How to evaluate an Internet resource / web site
There are a few things you must check when we look at the usefulness of the information on any website.
- Source of the website. Whose website is it ? How to contact the website owner/manager? (check the 'About Us' link that is usually provided on a web site to get this information). It is important to know about the source of the information, to get a sense of its authenticity
- What kind of web site - commercial, educational, etc. Educational sites or non-commercial sites may be more reliable, generally, since they are not trying to 'sell' you something
- What is the copyright of the content on the site? Is it providing information on free or paid or subscription basis?
- Features of a website: How useful a website is depends on how many different ways we can access the information and use it and view it. Can it be used by teachers, students, general public? The understanding of this will also help us determine how much we can use the content.
- Relevance: Often when we search, we may immediately share the first page we find, with others. However, it is important to read (at least quickly) the contents of the page, to help you get a sense of the relevance of the page for your purpose. Information use is very contextual and depends on its vintage as well. If the information is very old, we need to test for accuracy. For teaching-learning resources see if the information is for teachers or for children
- Use of multiple websites: Only one website will give us only one kind of information. Using more than one website will give multiple perspectives. We can also cross check and identify errors if any. For the same purpose, more the internal and external web links on a page, more useful it can be, since it can lead us to more resources. For teaching-learning resources, particularly check if the information is reliable by checking more than one website.
Bookmarks
Web browsers allow you to mark bookmarks, which are simply short-cuts to sites in the browser. You can book mark sites you visit often.
To add a bookmark: Go to Menu Bar and click the bookmarks and click on "add this to bookmarks" to save the current page as a bookmark. By default, new bookmarks are saved to the Unsorted bookmarks folder. ... If you want separate folder, you can also create as per your requirements.
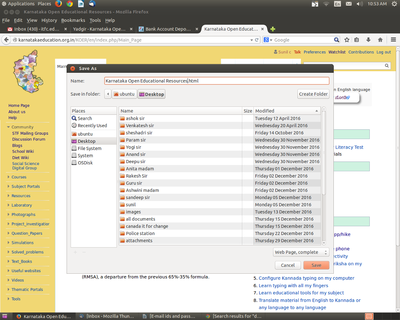
Save web page to use offline
After you have accessed the resources, you can save web pages offline to use without internet. To save the page, right click on the page and click on "Save Page As". In the save tab, you can give specific file name and in the file format you need to select "Web Page Complete" and then click SAVE. Now it will save html file with a thumbnail folder. By clicking on html file you can view web page offline.
Web tools
Apart from using search engines to search for information, there are several web tools which cater to different information requirements. These include on-line maps which provide map information (such as OpenStreetMaps or Google Maps), on-line dictionaries (such as Shabdkosh), digital albums (such as Flickr) translation (such as Google translate) etc.
Student activity time (2 hours)Your faculty would have demonstrated different kinds of websites above. In groups, look for websites in the different categories. In each group, use a search engine to access different websites on the internet. search and make a list of 3-5 websites. Enter these addresses in your note book and download information, consisting of web pages, image, videos, etc relevant to your topic. Search for resources connected to the topic you have identified. Open Wikipedia and search within Wikipedia for topics of your interest and the topic you have identified. References: Learn Firefox |
Creating your own personal digital library (PDL)
A personal digital library (PDL) is simply a folder containing a set of sub-folders and files on your computer, which contain information on a particular topic. You can store information on different topics of interest to you in different folders, which together constitute your PDL on your computer.
The PDL is 'personal' meaning it is available on your own computer, for your use any time. It is 'digital'; it is available in a digital format, which makes it easy for you to store, search and share. Most importantly, it is a 'library' meaning the digital resources are organised meaningfully, for you to easily access information when you want it. For your chosen topic, you can create a PDL, consisting of the set of resources downloaded from the GDL, in your folders and sub-folders. You can later create a 'meta document' for each topic, using a simple text editor, which will have information about the resources and the files stored in the PDL.
You can build such libraries on any topic you are interested in, and support your own self-learning in a structured manner. Since the internet has resources on almost all topics, you have an opportunity to keep learning on topics of your interest. The topic or area need not be only one of theoretical interest or only to build your knowledge. You can also work on building skills, there are likely to be videos available for helping you learn a new language, or even a skill like swimming.
You can share this personal digital library with your colleagues, by simply copying the folder containing the sub-folders and files, so that they can also benefit. When teachers share their personal digital libraries / resources from their library with their colleagues, cumulatively, it creates a rich and diverse resource environment. (You may already be sharing music and video files with your friends on your phone or computer, for entertainment, the PDL extends the same idea for self-learning and peer-learning).
There are a few steps in creating the PDL.
- Make a folder (this could be under your 'home' folder or your 'documents' folder) on the computer by topic, the topic name can be the folder name. Always give full and complete names to any folder or file, avoid using abbreviations or acronyms. This way, just reading the folder or file name will give you an idea of its contents.
- This can have sub folders for ‘Text’, ‘Image’ and ‘Audio Video’ for saving your save your text, image, audio and video files respectively. By organizing your files and folders carefully on any topic, you are creating what can be termed as a ‘Personal Digital Library’ on that topic. Having personal digital libraries allows you to access and re-use resources easily and effectively.
- You could instead create sub folders for different sub-topics for your topic and save your files based on the sub topic. For instance, the topic 'energy' could serve as the name of your folder, within which you could create sub-folders for heat, light, magnetism, electricity etc. You should think about the way you would want to access your library later, and create the sub-folders (and sub sub-folders) on basis of this hierarchy. Searching for files later becomes easier if you have categorised them and then organised them in folders based on these categories.
- As a teacher, you could also have the 'academic year' as the base folder, within which you could create the resource folders and sub folders, for topics connected to your teaching. This way, when you begin a new year (2017-18), you can simply copy the folder of the previous academic year (2016-17) with the new year (2017-18) as the folder name. You can then add, modify or delete files in the sub folders within this year folder as per your requirements for the new year.
- Access relevant resources - web pages, text files, images, animations, audio clips, videos, from internet
- Save these on relevant sub-folders in your folder.
- Create a 'meta' document which will provide your thoughts on the topic (you will learn how to create a text document in unit 2, so this can be done later)
- Copy links of the resources you find useful, and which you would like to refer to later, in your meta document
- Add your own comments, suggestions in the meta document, and connect the resources accessed and shared, with your ideas to create a resource document on the selected topic.
Student activity time 5 hours
References: Learn Ubuntu |
ICT for connecting and learning - Professional learning communities of teachers
Many professions have their own professional associations. These associations provide a forum for continuous interactions with fellow practitioners (peers) and allow methods of learning beyond the college or university. You would have learnt about social constructivism and peer learning. Teachers, as professionals too need to connect regularly to their peers, for sharing their experiences, practices as well as insights. They also need to be able to contact peers as well as mentors for seeking support.
While professional communities and associations have been there for a long time, ICT have made possible ways of connecting and communicating with one another simpler and more accessible. On-line communities are often a good way of continuing interactions beyond the restrictions of meetings of physical time and space, and can provide for learning beyond workshops. On-line communities can be mailing forums or discussion groups and can be accessed either through your phone or computer.
The National Curriculum Framework for Teacher Education (NCF-TE, 2010) talks envisions teacher education with the following key components: (i) collaborative networks for learning and sharing, (ii) continuous learning (iii) different paths and spaces for learning. It regards peer learning as an important component of Teacher Professional Development.
Professional Learning Communities is a recent method for continuing professional development and by providing teachers with peer support, it can be a sustainable method of development. You will form a ICT based learning community of all your classmates, and use this network over the course to share your ideas, experiences and learnings, seek support and feedback of classmates for collaborative learning.
Participation in online, email and mobile-based forums
Since the internet is a network of computers, you can send messages (called 'emails' or simply 'mails') from your computer to others, who can access it on any computer connected to the internet. Talking to a friend through Whatsapp or telegram chats, emailing or making a video call are just some of the ways in which the internet has changed the way we communicate with others. You can join other friends, form groups to learn about many things.
You may be using a 'free' (as in free of cost) email such as Gmail. You should know that your mails can be 'read' by the email provider Google. Just like Google retains your 'searches' information, it also 'machine reads' your mails, so that it can show you advertisements based on the content of your searches and mails.
Your mails may also be 'tapped' by authorised and unauthorised entities as it passes over the internet. Hence you need to take the maximum care of your digital information and be careful of what you share digitally. You should not assume that anything digital is automatically private and confidential, it may not be.
Using a webmail application - Gmail
Most of you will already have a Gmail or another mail account. You can use the Gmail handout for information on how to create a Gmail account.
Composing, sending and receiving emails
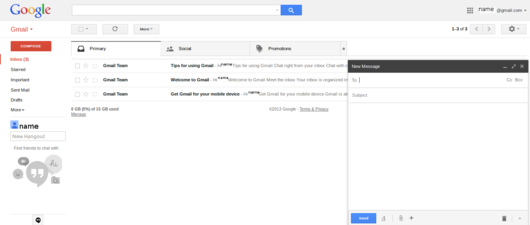
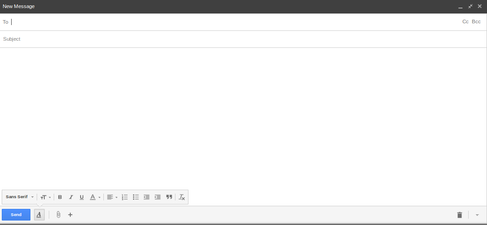
To compose a new message using Gmail, click "Compose". This can be found on the left panel,and is shown in the first image below. When you click on that you see a panel open for composing a new mail. The second image shows how you can start composing your new mail.
- Composing emails
Some basic features of the 'compose mail' form are discussed below:
- To: enter in an email address
- Cc: “Carbon copy” or “courtesy copy” another email address (not the main recipient; meant to keep others in the loop)
- Bcc: “Blind carbon copy” another email address (any email addresses entered here will be hidden from one another)
- Subject: a few words to describe what your email is about
- Body of the email: type your message. Click on attachment icon (next to send icon) to attach your local files(text files, images, etc.) with the mail and send it to the receipt. After you done all the above steps and if are ready to send your mail, just click on Send icon.
- To access your sent mails, click on Sent from the left side panel.
Checking mails and replying
Your Inbox displays all email messages you have received. By default, unread messages in your Inbox have a white background and display in bold lettering while read messages have a grey background and normal type.
Downloading an attachment
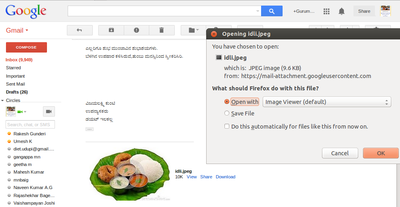
- A paper clip icon next to an email indicates that there is an attachment with the mail, as shown in the attached image
- To download an attachment in an email, open mail and scroll down the message and come to the file attached.
- You can either view or download the file (down arrow mark).
- Click on Download
- A window will appear Click on Save
- Choose the location where you want to save the file
- Click on Save to finish
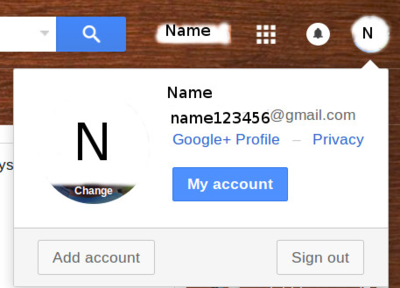
Sign out from the account
This is very important steps to secure your mail privacy. Logging out of your Gmail account is essential if you use public computers or even in personal computer. Your Gmail account can contain a lot of sensitive information, and signing out will help protect it.
- Click on your name or small circle with your starting letter of your user name, which displayed on top right side of your screen, as in this screen.
- Click on it and select sign out or logout.
Social networking
Social networking is another method of connecting people. Usually social networking platforms allow people to set up their profiles / create their own identities, and connect to other people sharing common interests, backgrounds or real life connections. While these are good for quick sharing of information and chatting, they are not well suited for academic discussions since, unlike a mailing list, the discussions are not 'threaded' (linked) which makes tracking a discussion difficult and retrieving a past discussion very difficult. Secondly, many social networking platforms do not charge the users, as they monetise user data. This can have larger privacy related concerns (as mentioned earlier, such privacy concerns also affect gratis mail services including Gmail). Many schools do not allow access to social networking sites, also because, it is often a source of cyber bullying.
Student activity time (3 hours)
References: Learn Gmail |
Equitable access to ICTs
Technology is a resource of society, hence we create a society where everyone can access it, interact with it, benefit from it and contribute to it. More and more people should be able to use ICT in a manner appropriate for their needs, for this, access to ICT should be treated like a public good, like public education or public health.
As you use the computers and Internet, the easy sharing of digital documents will seem quite powerful – instead of physically photo copying documents or recreating models of a device, making digital copies of the document or photos of the device is simpler and also almost free. Hence it should seem obvious that digital modes of information production and sharing would make resources easy to access, covering all kinds of digital items including content and software. However, there have been very strong forces that have worked against such easy sharing.
Paradoxically such sharing has been made difficult using technological methods as well as legal methods. Legal methods have been through releasing software or content using restrictive licenses, that forbid sharing or modifying (making these 'proprietary' instead of 'open'). Technological methods have been to not release the source code (in case of software), which is required for making modifications and by using techniques that prevent 'copy paste' processes. 'Proprietary' software which forbids sharing and customising is used by most ICT users.
One argument for restricting free sharing is that the creator needs to be compensated for producing the resource and instead of having the first buyer pay the entire amount of creation, seeking license fees from many users can reduce the costs to the first buyer and also increase the profitability for the creator. While this argument can have relevance in commercial transactions, in the case of education, where the free access to and sharing of learning resources is essential, using digital resources that do not have restrictive licensing would be necessary.
FOSS
Fortunately, in the case of software, there are free software communities that have developed software and released it on liberal conditions, that allow free sharing and modifying. Dr Richard Stallman, who was a professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, established the Free Software Foundation, which worked to develop software applications and released them under a 'General Public License' (GPL), which allows the user four freedoms – to use, study, modify and share. The GPL also insists that any changes made to a free software should also be released on same terms.
OER
Similarly in the case of content or learning materials, the 'open educational resources' (OER) movement aims to support creation of digital materials that allow the four rights – right to reuse, revise, remix and redistribute (called the 4 Rs).
Teachers often will need to contextualise materials (make changes as per their own needs), which copyrighted materials would not allow. Hence there is a movement to produce learning resources and make available with less copyright restrictions. The 'Open Educational Resources' movement aims to release materials with minimal restrictions, which will allow teachers to freely 're-use', 're-vise', 're-mix' and 're-distribute' materials (these are called the 4 Rs, the fifth R can be 're-tain'). Teachers can access available OER from the internet and create their own digital libraries on their computers for different topics of their interest. Teachers can release materials they create as OER, so that other teachers can give feedback as well as revise/refine the same to make it better quality. FOSS and OER movements aim at providing digital resources that are licensed to allow you to make copies. In addition, you can modify the software / content resource and share again. FOSS and OER, allow greater access to software and content, and hence are necessary to adopt and promote for equitable access to ICT.
Inclusive use of ICT
By allowing for different methods of representing information (in different formats, using different tools) and communicating, digital ICT provide diverse set of opportunities to support different (multiple intelligences) learning styles. Moving away from only the written word, to using images, audio and visuals to communicate understanding and making meaning allows for a more inclusive learning environment.
In addition, there are specialised hardware and software applications to support visually, hearing and speech challenged learners. Text to speech converters are useful for visually challenged such as the FOSS application ORCA, speech to text converters can help those who are unable to use the keyboard and mouse as input devices (these are available on mobile phones now for simple tasks like making calls, searching the net etc.). On most screens, the font size can be increased (usually by simply selecting CTRL ++) to the size required, which can help some people with poor vision.
Student activity timeParticipate fully in the digital world - by accessing, downloading, modifying and sharing digital resources.
References: Teachers' toolkit for creating and re-purposing OER using FOSS Ethical use of ICTYou will be learning to use ICT for many purposes. However, you should know that ICT use can be beneficial or harmful, and you need to use your judgement in the use of ICTs. Ethical challenges in the use of ICTs can arise in the following situations:
You need to be aware of these dangers and learn to avoid these, and help your classmates also avoid these. Plagiarising - copying resources created by others and representing it as yoursWhile it is easy to copy a resource from the internet and include in your own work without giving credit to the creator, it is an unethical practice. This is called 'plagiarism', the more familiar word is 'copying'. Referring to other resources, 'citing' them in your work, or adapting them to meet the needs of your work are ethical activities. This is called 'fair use' of materials created by another person. What is 'minor' copying or 'large' depends on the situation, and you need to use your judgement. In case of doubt, always discuss with your teachers, classmates and friends. One simple rule - use materials from existing OER sources, and give credit to the source, in your own document. Violating the 'license' associated with the resourceDigital resources, including software and content always have an associated 'license' of use. In case the software or content is licensed as 'proprietary', where the creator has all the rights, and has not given any rights to others, then using the digital resource is illegal, without paying the required license fee and unethical. Such use is called 'piracy'. You may find it technically very easy to just 'copy-paste' an article from the internet or copy a proprietary software program from another computer, or download a movie from the internet which is not licensed to be copied. All these would be unethical practices and must be avoided. For the same reason, your school computer lab must not have any pirated software. If you find any pirated software or content in the school computers, please do bring it to the notice of your teacher. One way of avoiding this unethical practice, is to use and promote Free and Open Source Software (FOSS) and Open Educational Resources (OER). It is ethical to use FOSS and OER. It is unethical to pirate proprietary software or content. Remember that if a digital resource has no explicit copyright clause mentioned, it means it is owned by the creator with no rights for others. Hence when you create a digital resource, please take care to explicitly mention that it is an OER. You can do this by providing the copyright clause such as - "Copyright - Creative Commons CC BY SA 4.0", you can mention this in the first page itself, below the title of the article. Ethical use of internetThe Computer Professionals for Social Responsibility has prepared the 'ten commandments' or ten rules for use of computers, some of which are listed below:
This can be pasted on your computer lab as 'Do's and Dont's of using the lab. Internet SafetyThe virtual world also can be as or more dangerous than the real world. Cyber bullying (including by students of other students), abusive communication, on-line fraud including transfer of funds from your bank accounts etc are common. A June 2011 Consumer Reports "State of the Net" survey "unearthed several disturbing findings about children and Facebook": One million children were harassed, threatened, or subjected to other forms of cyber bullying during 2010.
Apart from harm that may be inflicted by others through the internet, there is harm from excessive use of the internet. See Man treated for Internet addiction. South Korea, the country which has the highest density of internet use has internet deaddiction centres in more than 100 hospitals. Like any other resource, the internet needs to be used wisely, there is a danger of misuse, abuse and over-use. Please visit the following sites to learn about safe internet use
Apart from harm to yourself, the use of the internet can cause problems for your computer, through malware (software viruses), or spam (unwanted mails). Do not download any software or content to your computer from the internet, unless you have clear instruction from your teacher. Before clicking on any link, consider if that link may lead you to malware or any fraud. Avoid downloading any content, unless you are reasonably sure it is genuine, by only downloading content that is licensed as OER, you reduce your chances of downloading malware. Courtesy in email communicationIn case of emails, do not open any mail from an unknown person. Do not click on / download any attachment, unless you are expecting it, even if the same is from a known person. Secondly, always participate in email discussions with utmost courtesy and respect to others. The email medium is prone to 'flame wars' where members exchange angry and offensive mails. The email medium has many serious limitations compared to a face-to-face communication, since it is difficult to communicate ones feelings and thoughts fully and clearly through short / terse written texts. Hence you need to take extra care to not get caught in any such inflammatory or angry or offensive discussions. 'Trolling' is a process in which many one or more people may gang up together to intentionally make offensive and inflammatory responses. In your mailing network of fellow student teachers, the administrator must take firm actions (such as warning offenders, suspending posting rights etc) against members who communicate in offensive ways. Integrating with other courses in the programYou can access the global digital library for resources for all your subjects. On almost any topic, you are likely to find many articles and you will need to assess the academic value of any material before using it. The virtual forums formed with your cohort can be used to discuss topics relating to all your courses. Threaded discussions on any topic can over time, become a resource in themselves. Topics need not be very specific to the topics in your source books, but can be on broader issues or topics in any course. You can use the virtual forums to share your experiences and ideas, and also resources created by you for feedback from your cohort. Giving and taking feedback can in itself be a powerful academic process. While physically giving and taking feedback on your work can be quite difficult and time consuming, virtual forums can be an easy yet powerful way of doing the same. Student Portfolio
|