Difference between revisions of "Cycles"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Objective''': Understanding the different cycles that exist in nature and in our daily lives that govern the ways the biosphere functions. | '''Objective''': Understanding the different cycles that exist in nature and in our daily lives that govern the ways the biosphere functions. | ||
| − | + | Part 1: Age group 6-12 | |
'''Lesson 1:''' | '''Lesson 1:''' | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
Look at card below and make your own season watch card. Choose a tree and observe it through the year. | Look at card below and make your own season watch card. Choose a tree and observe it through the year. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Part 2: Age group 12-14 | ||
'''Lesson 7:''' | '''Lesson 7:''' | ||
Latest revision as of 22:42, 3 October 2021
Objective: Understanding the different cycles that exist in nature and in our daily lives that govern the ways the biosphere functions.
Part 1: Age group 6-12
Lesson 1:
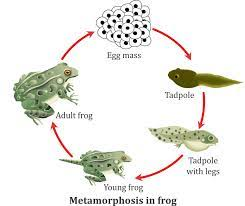
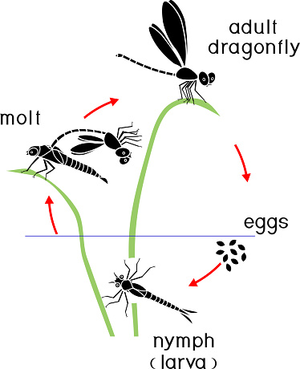
- Observe the following life cycles in a pond.Draw and label.
- Life cycle of a frog
- Life cycle of a dragonfly
- Compare what is drawn and what is in the picture and learn the keywords.
Lesson 2:
Lifecycle of a butterfly :
- Draw the lifecycle of a butterfly.
- Observe and name a plant/shrubs/trees that attract lots of butterflies . Eg :Singapore cherry
- Observe and name a plant/shrub/tree that has caterpillars(erukkam plant) .
- Observe and name a plant where you find eggs of a butterfly (Neem tree).
Note : Butterflies, bees and wasps play an important role in pollination. Draw the lifecycle of a flowering plant.
Lesson 3 :
Lifecycle of a flowering plant:
1. After drawing the life cycle of flowering plant in the previous lesson, observe a flowering plant . (Eg: Thanga arali , Chilly plant , Drumstick and Curry leaves)
2. Note down the observations.
Lesson 4 :
Food Cycle:
1.Draw the cycle of where the food we eat is coming from and where the food we eat is going to.( snapshot of child’s work as below : )
2.Take a simple lunch menu and trace back what are the ingredients of the menu 3.Find out what are the sources of the food –
- Plant or animal or sea.
- Parts of the plant-Stem/leaf/flower/fruit/root/seed.
3. Find out how many days does it take from the day seed is sown till the harvest is made.
4.Find out the recipe of the dish made from parents .Do a cooking activity if possible.
5. Draw the digestion system of our body and trace the path of the food from the mouth to anus.
6.Discuss how the human waste gets back to the earth and trace it’s journey.
Lesson 5:
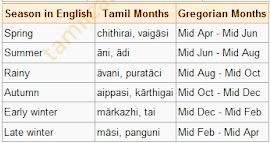
Tamil Season Cycle :
1.Using the tamil calendar ,draw the yearly seasonal cycle of your area. For example ,
*The rains in Thiruvannamalai occur in purataci (south west monsoon)and karthigai (Northeast monsoon )
Lesson 6:
Season watch of trees:
Look at card below and make your own season watch card. Choose a tree and observe it through the year.
Part 2: Age group 12-14
Lesson 7:
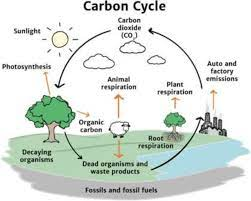
Carbon cycle :
- Look at the carbon cycle .
- Write down the small ways in which can you reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in your daily life.
- Eg: When you take food from the fridge , take it atleast one hour before so that the amount of heat is reduced. For shorter distances ,walk or use a cycle. Use degradable soaps rather than detergents
Note: Do you realize the one and only species which convert carbon dioxide into starch is a green plant?
Lesson 8:
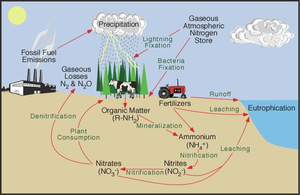
Nitrogen Cycle :
- In this cycle, observe the nitrogen fixation by plants.
- Name some plants that fix nitrogen in the soil.
- Interview an organic farmer and find out what are the crops that fix nitrogen and how do they alternate crops.
- In your body, find out how nitrogen is used for body functions eg: protein synthesis.
- Look at the labels of different products that you eat .Write down the names of the compounds that contain nitrogen.
Lesson 9:
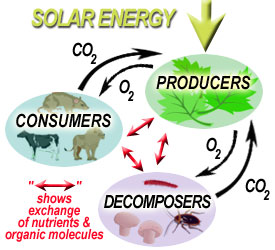
The cycle of Producer, Consumer and Decomposer:
- Write a paragraph about decomposers using the following keywords: dead decaying matter, moisture, nutrients , soil , breaking down .
- Write a paragraph on the role of fungal network for the growth of trees.
Lesson 10:
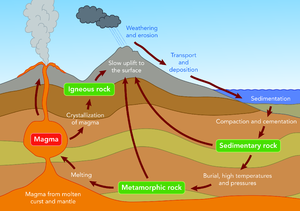
Rock Cycle:
- Find names of rocks that are found In your locality.
- Write down the different forms of weathering.(Eg In Tiruvannamalai hill which is made of granite rock , often we see peeling happening due to heat and cracks form through which water penetrates and the gap increases eventually breaking the rocks. Roots of fig trees penetrate through smaller rocks. On of the teachers observed how a Pachai kiluvai tree had broken the rock into two parts. Similarly can you observe and find names of trees which penetrate and break rocks.
Lesson 11:
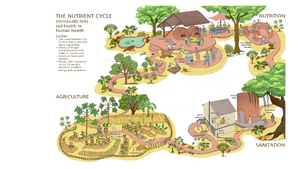
Soil Cycle:
- Take a handful of soil .Use a lens and write down what all you see in the soil.
- Connect to the components that you have observed with the given picture of the soil cycle. Discuss the same.